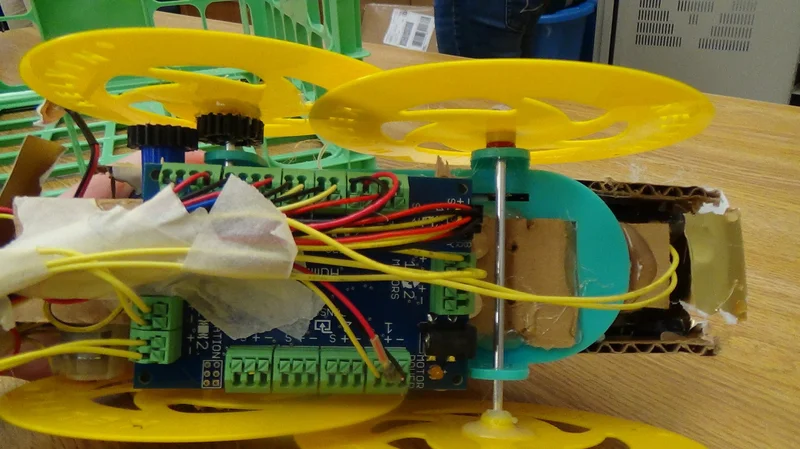
AMT Lab Contributor Wei Wei investigates the creative decisions and technological challenges behind the first large scale, Virtual Reality musical performance experience.
Connecting Communities Through Howlround's World Theatre Map
The Giving Pledge: A Start to Engage Tech Philanthropy
To understand why arts organizations have struggled to capture funds from tech billionaires, arts managers and development professionals would do well to recognize what philanthropic sectors they are losing these dollars to, and why. Armed with these insights, arts professionals can then adjust their strategies to better appeal to this new and growing donor segment.
STEAM Learning at the Carnegie Science Center
Moving the conversation around public education from STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math) to STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Math) has long beleaguered arts managers and arts educators alike. Defending the argument for arts programming and arts education can be difficult in the face of shrinking school budgets and a highly competitive grant environment. Particularly in a country that increasingly favors the hard sciences above the humanities, cultural pursuits, and artistic studies. Despite gains at the federal level with the new core arts standards, the STEAM caucus, and the first budget increase for the National Endowment for the Arts in years, it is still easy to feel defeated. The question remains, what can arts leaders and community organizers do at the local level to push the conversation in a positive direction?
Silicon Struggle: The Battle for The Bay Area Arts' Scene
If you told the average San Francisco resident 40 years ago that the art scene in the Bay Area would be gasping for life in 2015, they probably would have laughed in your face. But it is 2015, and that is the reality we are facing. The tech giants have moved in, and tension is building between the Silicon Valley community and its non-profit entities. In particular, arts organizations seem to be at an extreme disadvantage for a few reasons:
CREATE Lab: Creating Social Impact Through Empowering Communities
CREATE Lab creates multi-disciplinary learning experiences that allow communities to become technologically fluent. CREATE Lab’s novel combinations of visual arts and technologies provide a wealth of new potential tools to arts administrators and their organization. This article will introduce a few of the exciting projects that CREATE Lab is already testing in the Pittsburgh community, as well as access points for administrators and educators who are interested in implementing them.
Research Update: Crowd-Funding through Google
With the development of crowd-funding programs through companies such as Kickstarter, Indiegogo, and Patreon, artists have many new ways to generate both funding and visibility. Arts and culture organizations have a harder time competing with individual artists on these platforms. In an effort to assist these organizations as they try to change the world, Google now offers its own crowd-funding platform for nonprofit organizations: Google’s One Today.
American Association of Museums Trend Watch 2012
The American Association of Museums recently published a report titled Trends Watch 2012, Museums and the Pulse of the Future. According to AAM, the field of museology could beat to the rhythm of seven emergent practices in upcoming years. Namely, these are crowdsourcing, alternative social enterprises, public engagement, microgiving or crowdfunding, changing demographics, augmented reality, and new educational opportunities. Of these trends, crowdsourcing, crowdfunding, and augmented reality will be explored in detail as technology fuels their very existence while the arts nourish their popularity. Crowdsourcing

Museums of 2012 should not shy from “harnessing the crowd”, especially when that crowd is more than willing to engage in unique tasks and activities. The report cites examples such as the Smithsonian Museum, which asked the public to vote on “which examples of video games to include in its “Art of Video Games” exhibit. As the PSFK reports, even the New York Public Library sought help from the public in its effort to overlay historical maps “onto the open, modern-day map, drawing from the library’s expansive map database that includes everything from maps of building types for fire insurance purposes to agricultural maps of droughts.” The report mentions Wikipedians in Residence, Digitalkoot project, and the Children of Lodz Ghetto Project as other examples of engaging the online world in content publishing and editing, archiving (through gaming!), and even historical research.
For museums, crowdsourcing is a novel way to increase volunteering while capturing the interest of experts and community members alike. Yet, not all tasks lend themselves well to the phenomenon; the crowd is best utilized when tasks are fun, meaningful, or interesting, and require large amounts of individual input. Additionally, while crowdsourcing speeds up the pace and broadens the scope of projects, “it also increases the burden of oversight and quality control.”
Crowdfunding
When it comes to funding for the arts, not everybody (including the government) is willing to give a lot. But when a lot of people give a little, what emerges is the financially fantastic, win-win idea of crowdfunding. The report suggests that Kickstarter, Indiegogo, and Peerbackers can be used “to reach people who may never have heard of your museum and invite them to support projects ranging from acquisitions to exhibits to building expansions.”
 The report also points to the possibilities of mobile giving with the introduction of Google Wallet and Card Case. Another fundraising initiative noted is Philanthroper, a start-up that helps raise funds for non profits via “an e-mail each day featuring a 501(c)(3) organization that subscribers can choose to support with donations of up to $10.”
The report also points to the possibilities of mobile giving with the introduction of Google Wallet and Card Case. Another fundraising initiative noted is Philanthroper, a start-up that helps raise funds for non profits via “an e-mail each day featuring a 501(c)(3) organization that subscribers can choose to support with donations of up to $10.”
For a successful crowdfunding initiative, an organization needs to think beyond the incentive of tax deductible donations. The most successful Kickstarter campaigns involve people in their creation send them tokens of appreciation (often the end products themselves). Thus personalized, fun, and unconventional incentives are key to appeasing to the masses.
Augmented Reality
Reality limits the possibilities of what is, could be, and was. So augmented reality, in all its limitlessness, was introduced to help us imagine beyond what is. According to the report, “AR refers to a set of technologies that can layer digital elements—sound, video, graphics, even touch sensations—over real world experiences via mobile devices.”
 One of the examples noted in the report is Streetmuseum Londinium, an app developed by the Museum of London which lets visitors explore Roman London and “ provides soundscapes to accompany scenes of Roman life superimposed on the modern city and encourages users to brush away dirt by blowing into their iPhones, “excavating” virtual artifacts in the process.” Another example of AR, not noted in the report, but cool nonetheless was used by the Science Museum in London. For its exhibit, Making of the Modern World, the museum created an app using a 3D avatar of Top Gear host, James May, who explained the significance of the objects in the exhibition.
One of the examples noted in the report is Streetmuseum Londinium, an app developed by the Museum of London which lets visitors explore Roman London and “ provides soundscapes to accompany scenes of Roman life superimposed on the modern city and encourages users to brush away dirt by blowing into their iPhones, “excavating” virtual artifacts in the process.” Another example of AR, not noted in the report, but cool nonetheless was used by the Science Museum in London. For its exhibit, Making of the Modern World, the museum created an app using a 3D avatar of Top Gear host, James May, who explained the significance of the objects in the exhibition.
Augmented reality certainly opens up possibilities but as the report notes, there is a fine line between engaging visitors and overwhelming or confusing them. It also suggests that AR can be used to exhibit and exist beyond the walls of the museum. Layar, an app by The Andy Warhol Museum that lets “users to explore Pittsburgh and New York City through the eyes of Andy Warhol”, is one such boundary defying example.
Additional details and insight into all the other emergent practices can be viewed in the AAM report. While these trends may not necessarily define the future of museums, they certainly put them on the path to a new technological era. Museums, who says you can’t be both conservative and trendy?
Lessons from the Bronx
By now you may be aware of the Bronx Museum of the Arts' new ticketing initiative. If not, take a look at the Museum's Facebook status from March 30th: "Starting today, the Bronx Museum of the Arts will be Free to all. Thursday through Sunday, FREE! First Fridays! FREE. Whether you're 8 or 88, FREE! Getting Here: B/D train to 167th St (Unlike the Museum, the train fare is not free)."
In celebration of its 40th anniversary, the Museum announced just last month it would offer free admission to guests-- this coming at a time when student discounts, twofer deals, good coupons, and gas below $3.99/gallon are at a premium. According to Museum Director, Holly Block,
status from March 30th: "Starting today, the Bronx Museum of the Arts will be Free to all. Thursday through Sunday, FREE! First Fridays! FREE. Whether you're 8 or 88, FREE! Getting Here: B/D train to 167th St (Unlike the Museum, the train fare is not free)."
In celebration of its 40th anniversary, the Museum announced just last month it would offer free admission to guests-- this coming at a time when student discounts, twofer deals, good coupons, and gas below $3.99/gallon are at a premium. According to Museum Director, Holly Block,
With our immediate community being the poorest per capita in the nation, and at a time when many are struggling to pay bills…we don't want anyone to have to use (admission costs) as excuse not to visit us.
It is because of a grant from the New York Community Trust that the museum is able to offer free admission to the public- though the grant only covers admission costs up to 15 months. The Museum is hoping to secure a more permanent funding source to be able to continue to provide free admission to the public after those 15 months.
Not only does this reduce barriers of entry for Bronx residents, New Yorkers, tourists, and artists, but it also benefits the museum community at large. Many museums have implemented similar free admission pilot programs and have reported varying results. It will be interesting to follow up with the Bronx Museum at the conclusion of the 15 month, free admission period to review its attendance numbers and demographics during that time.
While snooping around for more information on the Museum’s new pilot program, I stumbled upon two special offerings at the Museum. How did I NOT know about these programs?!
1) smARTpo wer: In conjunction with the U.S. Department of State’s Bureau of Education and Cultural Affairs, the Bronx Museum administers this cultural diplomacy program. The program funds and provides travel opportunities for 15 U.S. artists to create and work abroad on a community-based art project. smARTpower supports “the development and implementation of community-based art projects that engage youth and other local residents, including artists. The projects are strongly encouraged to create a tangible legacy of the work accomplished through smARTpower in a variety of visual arts media…” The program is open to professional artists only with U.S. citizenship.
wer: In conjunction with the U.S. Department of State’s Bureau of Education and Cultural Affairs, the Bronx Museum administers this cultural diplomacy program. The program funds and provides travel opportunities for 15 U.S. artists to create and work abroad on a community-based art project. smARTpower supports “the development and implementation of community-based art projects that engage youth and other local residents, including artists. The projects are strongly encouraged to create a tangible legacy of the work accomplished through smARTpower in a variety of visual arts media…” The program is open to professional artists only with U.S. citizenship.
2) Artist in the Marketplace (AIM): Established in 1980, the program seeks to provide “networking opportunities for emerging artists residing in the New York metropolitan area" and to introduce "their work to a greater audience.” Thirty-six selected participants attend weekly seminars led by a faculty of specialists. Topics covered in these sessions “address areas of practical concern to artists including: career management and gallery representation; exhibition and public art opportunities; grant writing, copyright law, and marketing.”
It is a hopeful sign, especially in these financially trying times, when a non-profit arts organization remains so concerned with serving its constituents- accessibility for its local audience, professional advancement for its arts community, and greater cultural understanding in diplomacy efforts.
Cities Thinking Differently, Through the Arts
 The past couple of years have been rough on America’s cities. The recession, job losses, budget cuts, and more people moving to the suburbs have all resulted in less tax revenue and a sense of unease about their future. Through these struggles, the cities have to consider questions like: What steps can be taken to foster economic growth? How can we become a player in an increasingly competitive global marketplace?
The cities of the Rust Belt, however, have had it a little worse. Unlike booming cities like Phoenix or Houston, cities like Detroit, Cleveland, and Pittsburgh are losing residents, with a fear that population losses will continue unless something drastic is done to “save the city.”
The past couple of years have been rough on America’s cities. The recession, job losses, budget cuts, and more people moving to the suburbs have all resulted in less tax revenue and a sense of unease about their future. Through these struggles, the cities have to consider questions like: What steps can be taken to foster economic growth? How can we become a player in an increasingly competitive global marketplace?
The cities of the Rust Belt, however, have had it a little worse. Unlike booming cities like Phoenix or Houston, cities like Detroit, Cleveland, and Pittsburgh are losing residents, with a fear that population losses will continue unless something drastic is done to “save the city.”
But instead of looking to traditional approaches like building an expensive sports stadium, performing arts complex or shopping malls, residents in cities like Cleveland and Detroit are taking a different route: embracing what Grist calls “Rust Belt chic,” the gritty, industrial, working class roots that embody and define the cities. One of the ways these cities are embracing this new dynamic is through the arts, and proving that having a thriving arts city doesn’t require investments or new arts venues: sometimes, all you need is to do is tap into what makes your city unique.
Much has been made about the struggles that face cities like Cleveland, Detroit, and Pittsburgh. This “Rust Belt chic,” first dreamed up by the “I Will Shout Youngstown” blog, based out of Youngstown, Ohio, can be best described by Governing magazine:
“A certain fascination with places that have fallen on hard times like the Rust Belt…has taken hold. Part of it is the scruffy, industrial look. It may also be a rejection of cities with gleaming condo towers, bistros and boutiques that were once so trendy yet now seem so frothy and fake.”
In other words, instead of trying to compete with the New York’s and LA’s of the world for visitors and potential residents, think different.
Cities all across the Rust Belt are taking this approach. But what many cities are doing is taking a low cost and high reward strategy towards economic development, which includes the arts community in a big way.
One example, as I wrote about in a recent post, is Detroit, who is embracing the arts community by providing tools and equipment to up-and-coming artists, fostering a sense of community for new artists moving into the city, even as thousands of residents leave every year. Detroit has the furthest to go of any city on this list, but businesses have started to move back to the city, young people are starting to move downtown, and its art scene has become home to increasingly diverse and eclectic artists, seeking to make a name for themselves.
Our home town of Pittsburgh is thriving (as any of us Pittsburgh residents would certainly tell you), and part of that is due to a thriving arts scene, which is frequently cited as one of the best things Pittsburgh has to offer. Much of the decay and abandoned buildings caused by the steel industry leaving decades ago has been taken over by the arts community and transformed into art spaces. What used to be an abandoned warehouse is now an art gallery; what used to be a factory plant is now a mixed use performance space.
It is because of this determination and grittiness, the drive to think differently and transform existing spaces, which makes Pittsburgh a perennial power in “America’s most livable cities” lists, often taking the top overall spot, as it did in 2010.
Cleveland is another case study. City leaders have struggled to come up with catchy slogans in an attempt to draw visitors, but local artists and arts venues aren’t focused on what Cleveland can do to “catch up” with other cities; they’re embracing what makes them different.
The Next American City recently looked at what it calls the “creative allure of urban grit,” focusing on cities like Cleveland. Because in cities like Cleveland and other across the Rust Belt, “you’re forced to accept that shit happens, and with that comes a freedom to creatively make sense of what’s happening. That’s art in a nutshell: the burn to make meaning out of failed plans and ruin.”
Some local artists are doing just that. The Next American City looked at Cleveland artist Amy Casey, whose paintings offer a unique and real look at the city. Housing vacancy and abandoned industrial plants a huge problem in Cleveland; Casey draws paintings where houses are connected together by ropes, or industrial areas are marked by decay.
One cannot help but to notice the economic strife and abandonment that has taken part in these cities; but while some would find such a sight depressing, others see inspiration. Casey’s paintings, and many others throughout Cleveland, seek to symbolize both the struggles it faces going forward, and the opportunity that awaits them.
Cities like Detroit, Pittsburgh and Cleveland all have many problems, and no one is here to suggest that the arts can save them on their own. But while all three areas, and dozens of others, create economic development plans and seek to spur investment and population growth to cities long forgotten by their neighbors, the arts is a way to provide a short-term boost to lift spirits, provide inspiration, and instill a sense of pride to communities.
We know it will be a tough and long road back for these cities. But at the same time, embracing what many call “rust belt chic” is a way for these cities to focus on what makes them different and unique, and offer a taste of what people can expect from these faded, but not yet broken, great American cities.
The 2012 London Olympic Games and the Role of the Arts
 You may have heard: the 2012 Summer Olympics, the global 2-week spectacle that brings some of the best athletes from around the world to compete in over two dozen sporting events, is taking place later this summer in London, from July 27th through August 12th.
But what you may not have heard about are all the exciting and unique events that are intended to showcase the cultural and artistic diversity of London, expressed through art, through a series of exhibits, performances, galleries and shows. The hope, organizers say, is to leave a “lasting legacy for the arts in the UK,” and with millions of tourists visiting the city for the festivities, and billions watching around the globe, there may be no better opportunity for that kind of exposure.
You may have heard: the 2012 Summer Olympics, the global 2-week spectacle that brings some of the best athletes from around the world to compete in over two dozen sporting events, is taking place later this summer in London, from July 27th through August 12th.
But what you may not have heard about are all the exciting and unique events that are intended to showcase the cultural and artistic diversity of London, expressed through art, through a series of exhibits, performances, galleries and shows. The hope, organizers say, is to leave a “lasting legacy for the arts in the UK,” and with millions of tourists visiting the city for the festivities, and billions watching around the globe, there may be no better opportunity for that kind of exposure.
So while the games may receive the lion’s share of attention this summer, it is the British arts community that is hoping to have a more sustainable impact for years to come.
London’s art renaissance is comprised of two parts: the first, the London 2012 Festival, is taking place this year from June 21st through September 9th, and is largely centered on the Summer Olympics and the Paralympics that follows. It is part of a broader campaign, called the Cultural Olympiad, which is a multi-year effort that started in 2008 and is dedicated to showing visitors the best Britain has to offer in the worlds of art, dance, music, culture and more.
The London 2012 Festival is the more high profile project, and will be immediately noticeable to anyone who makes the trip to London for the games, as over 1,000 events are planned. Organizers are proclaiming that there are “10 million free opportunities to get involved,” and while the full list of events has yet to be revealed, there are already hundreds of shows and exhibits that have been announced. Perusing the website you can find such events as film festivals, comedy shows, concerts, carnivals, and fashion shows, some of which require tickets, but the majority of the events are free to the public.
One of the most notable events announced thus far is the Damien Hirst exhibition at the world-famous Tate Modern. In the world of film, a festival showing silent movies by home town director Alfred Hitchcock will be presented, alongside a live musical performance of the material.
My favorite part of the festival, however, and I imagine many others feel the same way, is the quintessential British playwright who will receive top billing. William Shakespeare will be in the spotlight, as the World Shakespeare Festival, which begins next Monday (April 23rd) and runs through September, will present almost 70 productions of Shakespeare’s plays in thirty different locations across the United Kingdom, including Scotland and Wales.
Organized by the Royal Shakespeare Company, organizers are calling it the “biggest celebration of Shakespeare ever staged,” with thousands of actors from around the world taking part in the project. In addition to the usual theatre presentations of Shakespeare’s work, there will be street performances and even amateur performances as well. The most ambitious part of the festival is the Globe to Globe project, where performers will act out all of Shakespeare’s plays, but each of them will be performed in a different language with different actors used for each performance.
It is important to remember that London is not only a sporting destination or the home to great museums and theatres: it is also what the Atlantic calls a “global cultural hub,” home to so many uniquely cultural people and neighborhoods. This cultural diversity will be on display through the festival as well, showcasing some of the best art from countries around the world.
One of the criticisms of the Cultural Olympiad and the upcoming London 2012 festival is the costs associated with such lavish productions, and estimates thus far for the total cost of both programs is about $154 million, no small amount for a country dealing with harsh austerity measures across the board over the last couple of years.
In addition to the overall government-wide austerity measures put in place by the British government, the games also come at a time of dwindling funds for the arts in not only just the UK, but all across Europe. I wrote recently about the impact that arts communities in Europe are facing, and while countries like Italy and the Netherlands have received the most attention, the cuts have hit the UK as well: as the New York Times reports, the British Arts Council saw its government funding recently reduced by 20 percent.
When the 2012 games were awarded to London, back in 2005, the economy was booming and expectations for both the games and the Cultural Olympiad were sky high, and lavish funding was promised. Of course, after the global economic recession hit in the fall of 2008, expectations were tempered, and both sides have adjusted accordingly.
One of the criticisms that critics have about the Summer Olympics is that it’s a sporting event that costs billions of dollars to produce, creates years of traffic problems and construction delays, and all the pageantry and spectacle that it comes with only lasts for two weeks, and then it’s gone forever (well, except for all the unused stadiums that come with it).
While the sporting part of the Olympics is only in town for those two weeks, it is the hope of organizers of both the London 2012 festival and the Cultural Olympiad that the impact that the arts community brings to the festivities, through art, dance, music, film, culture and so much more, has a lasting impact even after the games have ended and all the medals have been handed out. It may not be in place as long as a giant football stadium, but the impact on British culture is sure to last for quite some time.
Facebook, Alternative Bands and Acoustic Sessions @ the MFA
To me, this just about sums up the 21st century Millennial: Facebook invitations, exclusive access to acoustic sessions, alternative bands,  behind the scenes privileges, access granted only through social media and a little culture via the fine arts. To what pray tell could I be referring? Why, Boston’s Museum of Fine Arts’ (MFA) partnership with radio station WFNX, of course.
Since May 2011, the MFA Boston has been showcasing nationally acclaimed acoustic bands in its galleries. Each month, an alternative band and 35-50 lucky winners are selected to participate in the exclusive Acoustic Sessions series.
behind the scenes privileges, access granted only through social media and a little culture via the fine arts. To what pray tell could I be referring? Why, Boston’s Museum of Fine Arts’ (MFA) partnership with radio station WFNX, of course.
Since May 2011, the MFA Boston has been showcasing nationally acclaimed acoustic bands in its galleries. Each month, an alternative band and 35-50 lucky winners are selected to participate in the exclusive Acoustic Sessions series.
How does one get selected to attend? Here’s where the Millennial wins. The concerts are announced on the MFA’s Facebook page and live on WFNX Radio (tune in on 101.7 FM in the Boston area). Interested followers can submit an entry form on the MFA’s Facebook page or call in to the radio station to be selected.
How does it work? The MFA’s upcoming Acoustic Series concert on March 27th is advertised on its Facebook page in the following post:
The MFA and WFNX have teamed up to present some of the best alternative bands, live in the galleries and Kasabian plays next on March 27. You can only see them by “liking” us and entering to win tickets here or listening to WFNX.
According the program’s press release, the artists perform in various galleries- from the European Paintings to the Contemporary American Art room. Their performances are sound and video recorded. They are then shared online, both on the MFA’s Facebook page and WFNX’s webpage.
Just when you thought it couldn’t get any more Millennial friendly, the MFA throws in this added exclusive- the performing musicians’ participate in the Museum’s “Art We Love”
program. The musicians select their favorite work of art in the museum, explain why they chose it or its significance to them and are then photographed beside the work. The photographs are uploaded to the MFA’s Facebook page for all to enjoy
and explore, providing unique insight and exclusive information on the musicians.
It is a perfect example of how the collaboration between social media, the visual and the performing arts can enhance the public's artistic experience and engage even those difficult Millennials. Originally from the Boston area, I am proud to share the MFA’s innovative programming with those from away. But I am sure other museums and galleries are up to similar projects. What other museums and galleries have similar, or completely unique, social-media driven, collaborative programs?
TechSoup launches Annual Digital Storytelling contest!
Whether they know it or not, every organization has a story to tell. But sometimes, it just so happens that this story is lost amid the frenetic activities of day-to-day work, and soon finds itself sitting quietly in the old forgotten folder of organizational history. Well, the month of February is the time to retrieve that story and subject it to some digital editing. This is because TechSoup, an organization that enables non profits to achieve their mission through technological solutions, has decided that some stories are best told digitally!
Recently, TechSoup launched its Annual Digital Storytelling contest which, “combines professional instruction and friendly competition into a hands-on media-making project.” Over the month of February,“TechSoup Global will host a series of interactive events including Twitter Chats, live webinars, and trainings designed to help nonprofits produce a one-minute video or five-picture Flickr slideshow that tells the story of its organization.” Yes, a minute or five pictures is all you have!
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ccCwQeAo4l4
TechSoup will accept submissions through February 29th, and in March, a panel of judges will select the organizations with the very best videos and “take their digital storytelling to the next level.” Another interesting and fun aspect is the Audience Choice Award, where “winning and notable submissions will be screened in San Francisco and live-streamed online through SecondLife as a special “red carpet” event on March 28, 2012.”
TechSoup’s competition is beneficial to not-for-profit organizations because stories are one of the most engaging ways to raise awareness and gather support. If an organization has a compelling story, people will listen. Better yet, if an organization can narrate it digitally, people will not only listen but they will also share it! And if the vast and ever expanding YouTube community is pleased, it might just go viral!
So non profits, make haste! You have a month and at most, a minute!
The Rise of Online Philanthropic Contests
 Over the past couple of years or so there has been a steady rise in the phenomena of competitive voting contests for not for profit organizations to receive grants for projects or operations. These contests are run by large corporations as well as not for profit groups. Examples of corporate contests take different shapes such as Pepsi's with the Pepsi Refresh Project which gives grants ranging from $5k to $50k based on competitive community voting toChase Community Giving which touts donations over $600 million dollars through Facebook contests. The National Trust for Historic Preservation has similarly put contests into place by granting to various historic restoration projects based on the number of votes they receive online.
Over the past couple of years or so there has been a steady rise in the phenomena of competitive voting contests for not for profit organizations to receive grants for projects or operations. These contests are run by large corporations as well as not for profit groups. Examples of corporate contests take different shapes such as Pepsi's with the Pepsi Refresh Project which gives grants ranging from $5k to $50k based on competitive community voting toChase Community Giving which touts donations over $600 million dollars through Facebook contests. The National Trust for Historic Preservation has similarly put contests into place by granting to various historic restoration projects based on the number of votes they receive online.
Whether these contests sit well with critic's ethical concerns or not, the volume of web traffic generated for the recipients, the donor organizations, and the organizations who compete but do not win is remarkable. According to Pepsi, the most recent contest in the fall of 2011 garnered more than half a million distinct registrations with over 3.5 million votes counted on the Pepsi site alone. If you aggregate this number with all of the site visits, social network hits, and emails then you have a truly noteworthy phenomena.
Why are people so invigorated by these contests? There are less time intensive ways to earn money in aggregate. One can point to the idea that the contest is a game and the competition itself is what people are engaging in more than the philanthropic cause. It could also be argued that the community effort of building a team to go online and vote for the cause for multiple days has an intrinsic value as well and that by the simple act of building this team you are building and drawing constituents deeper into the arts community.
As these online contest continue even more organizations are starting to do them. The Humane Society recently used a online photo contest to raise hundreds of thousands of dollars, the Case Foundation has been running a voter based contest for years, and American Express has also run contests in the past.
The following are some tips that have been gleaned from articles and criticism of various contests mentioned previously:
1) Make sure that the contest aligns with your mission. By diverting resources for a potential pie in the sky pot of money you can detract from your organization's true work.
2) Ask what your organization can gain from competing for these pots of money? Set forward goals of community building and identify volunteers to assist with these aims.
3) If you are going to market this to your patrons identify your budget for staff time and delegate a reasonably proportional amount of money to pursue getting the word out.
4) Don't start mid-steam. Almost all winners of these contests have strong starts and once you are behind in the voting it is hard to keep up. If you see a contest in progress that you would have liked to take part in simply put it on your calendar for an effort next year as your opportunity may all ready have passed.
‘Tis the Season for Getting Those Millennials to Give
With the holidays upon us, Baby Boomers and Generation X'ers selflessly reach deep into their pockets, beyond the lint, to give what they can afford  to not-for-profit organizations. But what about the Millennials? How do we get the generation classified in the media and not-for-profit circles as self-absorbed and self-interested to donate? The Case Foundation presents “Millennial Donors Report 2011,” a survey and summary of the motivations and preferences of the Millennials when it comes to making a donation.
to not-for-profit organizations. But what about the Millennials? How do we get the generation classified in the media and not-for-profit circles as self-absorbed and self-interested to donate? The Case Foundation presents “Millennial Donors Report 2011,” a survey and summary of the motivations and preferences of the Millennials when it comes to making a donation.
Earlier this fall, I posted on the best practices for engaging Millennials, the generation of 20 to 35 year olds that is dramatically affecting the way organizations market their brand and product. So in the true spirit of the holidays, let’s take a look at what may seem like an impossible task: getting the Millennials to donate.
The report surveyed about 3,000 Millennials ranging in age from 20-35 years old. Perhaps the most revealing find of the survey is the following: above all, Millennials value trust. A whopping 90% of Millennial donors surveyed reported they would stop giving to an organization if they had any reason not to trust it. What does this mean for not-for-profits? Build personal relationships with your donors and clearly define where and how the donation is used. Because the Millennials are young professionals, students and young adults with limited funds, they are most concerned their donation of any size will be utilized responsibly. Establishing trust with Millennials will encourage future giving and ensure a long-standing donor-organization relationship.
The report is divided into the categories: giving, giving motivators, special events, communication, volunteering, young professional groups and taking action, as they relate to Millennials. Here is a breakdown of the key findings and the implications for your organization
1. 93% of Millennials gave to not-for-profits in 2010
What this mean for you: Millennials tend to make small donations to multiple organizations, as opposed to the Baby Boomers or Generation X that are loyal to a single organization, gifting large sums of money. They ARE donating, which I am sure comes as a great surprise to the many who tag this generation as plugged-in and tuned-out to the rest of world.
2. An online search using an engine such as Google is the #1 way Millennials get information about a not-for-profit organization
What this means for you: How does your organization appear in a Google search? Millennials often base their decision to donate on the organizations appearance in an online search. Pay attention to your organization’s description on search engines.
3. 57% of Millennial donors gave in response to a personal ask
What this means for you: Though the Millennials seem to inhabit the online space more than their physical space, they are surprisingly more inclined to donate in response to a personal ask. However, that is not reflected in their preferred method of donating- 58% of Millennial donors reported they prefer to make that donation online. An unsuspected dichotomy…
The least preferred methods of the Millennial donors are via mobile applications (4%), the phone (5%) and text message (5%).
Reference the graphic “How donations were made vs preferences” in the report to be sure your organization is providing Millennials with the correct channel for giving that addresses their preferences (the most popular of which are online via your website, email, a donation site, or a personal request). Do not let a Millennial donor slip away by simply neglecting to provide the giving tool that best meets their preferences.
4. 79% of the Millennials surveyed reported having volunteered at least once in 2010
What this means for you: Just as expected of the Millennials, they are strapped for time as young adults and professionals. Thus the resounding reason for not volunteering is lack of time. Millennials are not interested in ongoing volunteer commitments. They prefer one-time, convenient volunteer activities. And obviously, they prefer to volunteer with friends than alone- the ultimate trademark of the Millennials. Of those surveyed, 61% reported they would prefer to volunteer with friends and family as compared to the 44% that indicated they prefer to volunteer on their own.
Get creative with the volunteer opportunities you present to the Millennials. They should be convenient, meaningful, group-friendly and perhaps provide an opportunity for professional development. As we saw when considering how donations are made, Millennials respond favorably to person-to-person contact and requests. Do not hesitate to simply ask Millennials to donate their time. As it turns out, 45% of the respondents reported their reason for not volunteering as never having been asked. So ask away!
5. 85% of Millennial donors are motivated to donate by a compelling and meaningful mission or cause, while only 2% of Millennial donors are motivated by a celebrity endorsement.
What this means for you: We already know Millennials crave meaningful content. They Tweet, re-Tweet and post moving videos, inspiring quotes and stirring news reports. Your website can be a perfect tool for tapping into the Millennials need for meaningful content. Share real-life, specific stories of how a donation supported your cause and not-for-profit. Invite the Millennials to be a part of meetings and discussions regarding the inner-workings of your organization and your strategic plan for the future. Millennials crave meaning, worth and inclusion. Invite them to collaborate with you and they will trust your organization.
The report provides cutting-edge research, insight and practical solutions for attracting and developing relationships Millennial donors. As researchers slowly uncover the hidden truths of these mysterious, influential Millennials and their relationship with the not-for-profit sector, we here at Technology in the Arts will continue to bring you the breaking news!
The Walker, venturing into online magazine style content
 The Walker Center in Minneapolis has a new website that has broken the mold and is venturing into offering content in a way that could help define a new paradigm of online content for large arts organizations. As the executive Director states in her press release: "The intent of the new site is to make visible our role as a generative producer and purveyor of content and broadcast our voice in the landscape of contemporary culture."
The Walker Center in Minneapolis has a new website that has broken the mold and is venturing into offering content in a way that could help define a new paradigm of online content for large arts organizations. As the executive Director states in her press release: "The intent of the new site is to make visible our role as a generative producer and purveyor of content and broadcast our voice in the landscape of contemporary culture."
By becoming broader purveyors of arts knowledge and information The Walker makes itself more relevant in the broader context of the arts across the country. The expertise that was only available through a visit to a lecture, through a docent on a museum tour, or a talk-back during a performance is now available through the we interface as the Walkers experts are now the gatekeepers for the online content. Thus the reach of the organization becomes multiplied by those people who share content and the organization.
This platform has the potential to lure entirely new audiences through the principle that traffic online follows quality of content. Also by revealing the values of the artistic staff of the organization The Walker is potentially connecting with like minded individuals in the arts community across the world. This in turn could make them into a destination city for arts tourists. By using the multi-disciplinary focus of the institution they are harnessing the the trend but by putting it online they are making it about the global dialogue and making themselves a shining example of what is to come.
The Fight over Net Neutrality is Far From Over
Last month, I wrote about what I consider to be the most important public policy issue affecting the arts/technology community, the issue of net neutrality. Since then, a wave of new developments have shifted the playing field and ratcheted up the fight over what is quickly becoming one of the most contentious policy issues in all of Washington. With the new FCC regulations slated to go into effect this Sunday, the legal and political wrangling over the issue is far from over, and the very future of the Internet as we know it is at stake.
First, a quick overview: the issue of net neutrality has received a fair amount of coverage recently because a new set of regulations passed by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) last December are set to go into effect this Sunday, November 20th. The regulations primarily do three things: they prohibit broadband providers from blocking lawful web traffic; require a greater deal of transparency from broadband providers regarding their network practices; and most importantly, require broadband providers to not discriminate in transmitting lawful network traffic over consumers’ internet service.
arts/technology community, the issue of net neutrality. Since then, a wave of new developments have shifted the playing field and ratcheted up the fight over what is quickly becoming one of the most contentious policy issues in all of Washington. With the new FCC regulations slated to go into effect this Sunday, the legal and political wrangling over the issue is far from over, and the very future of the Internet as we know it is at stake.
First, a quick overview: the issue of net neutrality has received a fair amount of coverage recently because a new set of regulations passed by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) last December are set to go into effect this Sunday, November 20th. The regulations primarily do three things: they prohibit broadband providers from blocking lawful web traffic; require a greater deal of transparency from broadband providers regarding their network practices; and most importantly, require broadband providers to not discriminate in transmitting lawful network traffic over consumers’ internet service.
While not perfect, these regulations are an important step to ensure that the concept of the “open Internet,” or the idea that all internet traffic is treated equally, continues going forward. Simply, it would preserve open Internet access for consumers, and not allow telecommunications companies to discriminate certain types of data as they see fit.
With the new regulations slated to go into effect shortly, Republicans in Congress have sought to overturn the rules, arguing that they go too far and that new government regulations are not necessary. This past Thursday, the Senate failed to round up the votes necessary to pass a resolution overturning the rules, failing on a party line vote of 52-46, with Democrats voting in the majority to stop the bill from going forward. The Republican-controlled House voted in April on a similar bill, which passed by a vote of 240 to 179.
The opposition in Congress stated that they also believe in the concept of an “open Internet,” but felt that such regulations were better written by Congress themselves and not the FCC.
Supporters of the new regulations, including the FCC, claim that the rules bring a degree of certainty to the internet community. In a statement, the FCC stated that “any effort to disrupt or unsettle that certainty, which has been widely supported by industry, will only undermine innovation and investment in this space.”
Even if the Senate had passed the legislation, President Obama had vowed to veto the bill, ensuring that any legislative efforts to roll back the regulations will fall short of success at least through the 2012 election.
The real immediate fight, however, over the regulations will be fought in court. Several telecommunications companies, most notably Verizon, have pending lawsuits seeking to nullify the regulations, claiming the federal government and the FCC do not have the authority to exercise regulatory power over the Internet. Attempts by the FCC to regulate the internet in the past have failed in the courts, so there is legitimate concern that the current case may meet the same fate.
In addition to concerns over potential content discrimination, there are other areas where telecommunication companies may seek to change their business practices if the regulations do not go into effect. The most common concerns are over higher premiums being charged for faster data speeds, or deliberately slowing down speeds for specific websites or services that may compete with the firm providing the internet access.
As I said last month, the issue of net neutrality impacts all communities, and many of the innovative and inspiring new art works and technologies we have highlighted here on the blog in recent months stand to be impacted if efforts to weaken the regulations are successful. Innovation is best achieved when entrepreneurs, artists and managers have the freedom to use technology to share their art with the world, and the openness of the Internet since its inception has facilitated countless new art forms and inspired a new generation of artists. It would be a shame to see that kind of progress stifled at the hands of Congress or the court system.
After the defeat of the Senate bill, the White House released a statement, saying that “it would be ill-advised to threaten the very foundations of innovation in the Internet economy and the democratic spirit that has made the Internet a force for social progress around the world.” As the fight over net neutrality moves forward and the regulations go into effect on Sunday, it’s important to remember that a free and open Internet is in the absolute best interest of the arts community, and is worth fighting for. That’s a bipartisan belief that everyone in the arts community can appreciate.
Art Viewed Through the Prism of 3D Technology
 On a typical trip to the American film multiplex these days, you are instantly greeted with the latest 3D films the studios have dreamed up. A market once reserved for the likes of advanced science fiction pictures, the technology has been stretched to now include nearly every major release. Given this barrage of often mediocre films, one would be hard-pressed to not grow tired of a technology still in its relative infancy.
3D technology, however, is not just limited to feature films. In Montreal, a cinema has embraced 3D technology and is using it to provide its audiences with floor-to-ceiling views, advanced speaker systems and a 360-degree view of stunning works of art.
On a typical trip to the American film multiplex these days, you are instantly greeted with the latest 3D films the studios have dreamed up. A market once reserved for the likes of advanced science fiction pictures, the technology has been stretched to now include nearly every major release. Given this barrage of often mediocre films, one would be hard-pressed to not grow tired of a technology still in its relative infancy.
3D technology, however, is not just limited to feature films. In Montreal, a cinema has embraced 3D technology and is using it to provide its audiences with floor-to-ceiling views, advanced speaker systems and a 360-degree view of stunning works of art.
The Satosphere theatre, as reported by AFP, is housed inside a giant silver dome in the city of Montreal, and is offering its audiences a unique way to enjoy the arts. The technology behind the cinema is impressive: measuring 18 meters in diameter, the dome has eight video projectors that display images all along the walls, encircling viewers and creating a truly immersive environment. Along with the projectors, the theatre also includes over 150 speakers, creating a truly cinematic experience.
And the best part of the experience? No bulky 3D glasses are required to enjoy the show.
AFP recently offered a behind the scenes look at the theatre, which you can view here.
The first show to display the technology, “Interior” by Marie-Claude Paulin and Martin Kusch, took place last month and wowed audiences both visually and sensually. With many more performances planned in the months and years ahead, the technology affords artists a new kind of opportunity not yet seen before.
The possibilities here are endless. Imagine an art show where attendees can become part of the experience, interacting with other attendees in a virtual exhibit. Or imagine being lifted to another time period or environment, surrounded by a 360-degree image of an architectural monument, barren deserts or idyllic beaches.
In addition to the opportunities for the arts community, other fields are also taking a look at the technology and seeking ways to possibly integrate it into their industries as well. Developers, hospitals, architects and many others are imagining ways to use 360-degree views to transform the way government officials, tenants, patients and more view planned projects or improvements, offering a way for people to experience a drawing or rendering in a visually immersive way before something is built.
The researchers behind the technology have no plans to just stop at immersive and interactive art shows. One of their current projects is developing a six-lens camera that uses software to merge images together, creating a seamless way to film 360-degree films.
The people behind the theatre are calling the experience “cinema for the 21st century” and “a playground for the next century,” and I’m inclined to agree. As it relates to the arts community, I can only imagine the countless creative ways and uses for a technology such as this; if the technology becomes inexpensive enough to spread worldwide, it’s quite possible it could usher in an entirely new era of artistic expression.
So the next time you leave the movie theater, disappointed with the “3D” technology in films like “Harold and Kumar” or “Puss in Boots,” remember that there are far more innovative uses for the technology being embraced all over the world, often at a significantly higher quality, perhaps headed our way very soon.
Building online community: sketchcrawl.com
Seven years ago Enrico Casarosa, an artist working for Pixar went on a pubcrawl. He writes that the spirit of community inspired him to create a community for visual artists that he called Sketchcrawl. The first Sketchcrawl happened in 2004 in over 20 locations in six countires. Since then, there have been 33 Sketchcrawls and the event has grown to almost a hundred locations in over 20 counties and now has a website sketchcrawl.com. The community now has over 3000 members and is still growing. At first, only Enrico was moderating, but Sketchcrawl has since grown to have numerous other worldwide administrators organizing participation and the community has strong leadership in both Asia and Europe as well as in North America.
A Sketchcrawl is a day predetermined thoughout the world, where artists young and old, professional and amateur pledge to sketch for anywhere from 20 minutes to 8 hours. The results of the event day are posted online for the whole worldwide community to see. There are some true gems in these online galleries. Participants speak of both the reward and difficulty of committing to draw for an entire day. They recount the lucidity that comes from a full day of observation and moving from subject to subject. They also comment on the difficulty of focusing their attention for so long. Side by side, these artists are creating a community through a shared experience and their love of art. Alongside their peers the collection of images lead us through a sense of movement throughout the day and objects and people that once were ignored as mundane become visible and interesting.
This community, built through a mutual love of the arts, is a strong sign of the growth of the arts online and should give the arts community at large hope for the future in the face of declines elsewhere. The next Sketchcrawl is on January 21, 2012. It is easy to sign up and there are also multiple social network sites for the community at large and for individual city groups.
What Makes Me, innovation from Down Under.
This website is called “What Makes Me”. There are three different sections: What Makes Me, What Makes You, What Makes Us. Each person claims a cube, a cleverly designed multimedia enabled object online and they decorate it with their images, video, and audio files. Each one is very different. The first twelve entries talk about why each individual loves a certain art form or forms - whether it be dance, circus arts, graffiti or something else. All of them are touching and told from the heart. There’s a retired nurse that found out her next door neighbor was a circus performer and has since fallen in love with the circus. There’s a professional rugby driver who drives around looking at the graffiti all over the city. There’s a professional cook who while catering a party, discovered dance for the first time and has since developed a personal relationship with the choreographer.
The common thread that runs between most of these testimonials is the personal connection built with a specific artist or the arts in their neighborhood. It’s about relationships, rather than facilities, and community as the key to these relationships.
The idea around this project was to counteract the perception that the arts in Australia are “associated with images of snobbery and inaccessibility”. The project is run by a company called Wanted Digital and initiated by the Australia Council for the Arts. The participants of What Makes Me are cooperating to build something together- it’s a game. A game that is getting the attention of philanthropic organizations in the US. Wolf Brown recently used this interactive project as an example of participation in the arts in their recent study commissioned by the Jame Irvine Foundation “Getting In On the Act - How arts groups are getting opportunities for active participation”.
What Makes Me is worth taking a second look at. The project engenders enthusiasm that isn’t created from simply being a spectator. Anyone in Australia can be a part of it and there is a hefty presence on the site from diverse populations with Aboriginal people, the disabled, and immigrant communities being well represented. Participants post links to their cube, to their facebook, to their twitter, to other social media sites. The individual act of creation combined with the community have a ground swell effect and foster even deeper love for individual artists and the arts contributions to the community.