AMT Lab contributor Mandy Ding looks into how museums are starting to use this trending technology.
Art + Code: Key Takeaways From the Weird Reality Conference
Artificial Intelligence and The Museum Space
Putting the “Arts” in “Artificial Intelligence”
Artificial Intelligence Absurdism!
Robotics, the Changing Nature of Work, and the Arts
An Introduction to RFID Technology
Radio Frequency identification technology (RFID) is nothing new, and many museums are already using it for inventory and security of their pieces. If organizations already have the technology, there are boundless opportunities as to how they can use it to increase efficiency and enhance the visitor’s experience. But how does this new technology work?
Intro to Beacons for Arts Managers
Connecting the real and digital worlds, beacons will prove to be excellent pieces not only for marketing and general propaganda about your specific location, but as informational tools in your local museum or performing arts company. Beacons focus on the consumer, the integral part to any organization regardless of industry. So far, beacons are most common in the retail world, but they can easily be transferable into other industries, like the arts. That’s why you’re here today. Beacons could transform your organization, and I’m here to navigate you through this process in an understandable way.
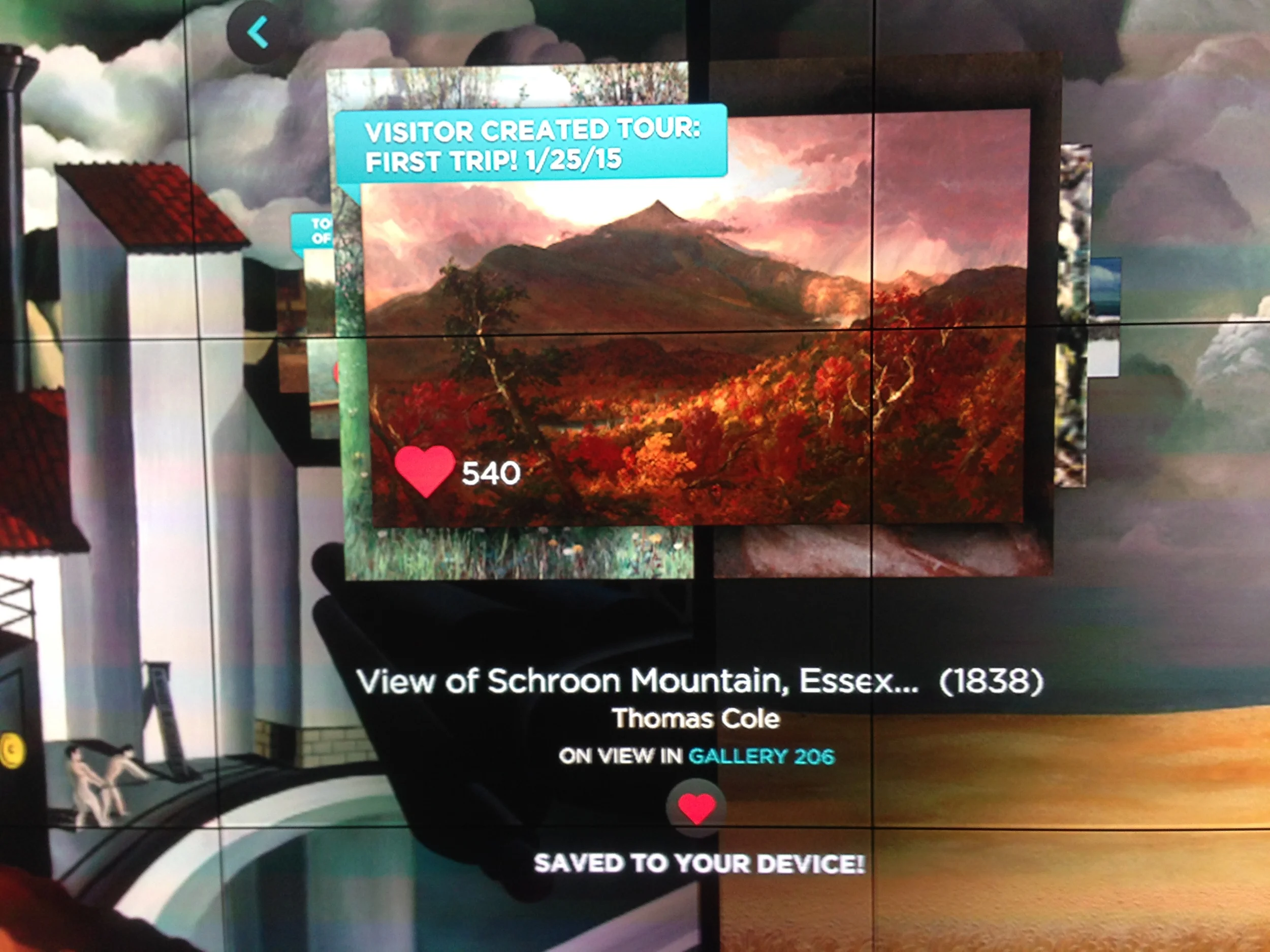
Gallery One: Engaging Audiences Infographic
How do you learn best about art? Maybe you lightly browse, interact with friends, or get right in the middle of the action. There are multiple ways to engage with and explore art forms, however cultural institutions may not always program to meet these needs.
The Cleveland Museum of Art's Gallery One activities, on the other hand, were designed with people's learning needs and preferences in mind. In this article I apply WolfBrown's Making Sense of Audience Engagement Audience Typologies to the different initiatives to see how learners can interact with the the Art Lens App, Collection Wall, Interactives, and Studio Play at the CMA.
The Giving Pledge: A Start to Engage Tech Philanthropy
To understand why arts organizations have struggled to capture funds from tech billionaires, arts managers and development professionals would do well to recognize what philanthropic sectors they are losing these dollars to, and why. Armed with these insights, arts professionals can then adjust their strategies to better appeal to this new and growing donor segment.
STEAM Learning at the Carnegie Science Center
Moving the conversation around public education from STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math) to STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Math) has long beleaguered arts managers and arts educators alike. Defending the argument for arts programming and arts education can be difficult in the face of shrinking school budgets and a highly competitive grant environment. Particularly in a country that increasingly favors the hard sciences above the humanities, cultural pursuits, and artistic studies. Despite gains at the federal level with the new core arts standards, the STEAM caucus, and the first budget increase for the National Endowment for the Arts in years, it is still easy to feel defeated. The question remains, what can arts leaders and community organizers do at the local level to push the conversation in a positive direction?
Silicon Struggle: The Battle for The Bay Area Arts' Scene
If you told the average San Francisco resident 40 years ago that the art scene in the Bay Area would be gasping for life in 2015, they probably would have laughed in your face. But it is 2015, and that is the reality we are facing. The tech giants have moved in, and tension is building between the Silicon Valley community and its non-profit entities. In particular, arts organizations seem to be at an extreme disadvantage for a few reasons:
CREATE Lab: Creating Social Impact Through Empowering Communities
CREATE Lab creates multi-disciplinary learning experiences that allow communities to become technologically fluent. CREATE Lab’s novel combinations of visual arts and technologies provide a wealth of new potential tools to arts administrators and their organization. This article will introduce a few of the exciting projects that CREATE Lab is already testing in the Pittsburgh community, as well as access points for administrators and educators who are interested in implementing them.
Research Update 1: How Technology Supports Collaborative Artistic Projects
Picture a producer preparing for the upcoming world premiere Contemporary Color, “a pep rally pop music mashup.” Conceived by David Byrne and commissioned by Luminato Festival and Brooklyn Academy of Music, Contemporary Color will bring together artists such as Nelly Furtado, St. Vincent, and Ira Glass, 350 performers, and a 15 piece band for its world-premiere performance in Toronto this summer. Not only are the artists, performers, and musicians all located in different cities across North America, great distances also separate the designers, technicians, and other producers. To coordinate the project across these distances, the producer relies on online collaborative tools to orchestrate the project from pre-production to post-production.
Attendance Trends: A Case for Technology in Museums
How Museums Are Dealing With New Media Art: Part 1
When talking about new media art, there is no single definition. According to a 2001 research study by the Rockefeller Foundation, media artworks can be defined according to nine common elements: fluidity, intangibility, liveness, variability, replicability, connectivity, interactivity, computability, and chance. New media art is a very general and broad category and includes many subcategories. Among these, net art, digital art and plurimedia art are the most common within the visual art field. Nevertheless, the meaning of new media is constantly evolving.
Promoting Digital Media Art through Digital Media tools
In our technology-stuffed world, the difficulties faced by video artists seem paradoxical. Due to high up-front costs, and the difficulty of handling and selling digital technologies, established institutions such as art galleries and museums often shun their work. Artists may look at the entertainment industry as an alternative, but find themselves unfulfilled, as musicians typically come first in these sorts of collaborations.
The Hello Cube at the Tate Modern: A Tweetable Installation
An interactive installation at the Tate Modern caused a wave of twittering and tweeting this past weekend. People often tweet about artworks but can one tweet at an artwork? And will the artwork tweet back? The Hello Cube, an interactive installation at the Tate, answered all of the above in no more than 140 characters. Even more twitterrific was how the dynamic installation continually changed its patterns and colors in response to individual tweets.
 The Hello Cube was the centerpiece for the Infinite Kusama Project, which centered on engaging younger audiences (ages 16-25) with Kusama’s work. Described as “a day of the immersive, the hallucinatory, and the expansive,” the project consisted “of a range of workshops designed to take you closer to Kusama's distinctive visual universe.”
The Hello Cube was the centerpiece for the Infinite Kusama Project, which centered on engaging younger audiences (ages 16-25) with Kusama’s work. Described as “a day of the immersive, the hallucinatory, and the expansive,” the project consisted “of a range of workshops designed to take you closer to Kusama's distinctive visual universe.”
The installation got its very own twitter account where users were prompted to tweet at it with commands such as “red love pixelate” or “blue cells faster." I got a tweet response from The Hello Cube within seconds, accompanied by an image of the compositional changes that had occurred in its mirrored inside due to my somewhat imperative commands! Over the course of the weekend, The Hello Cube obliged several thousand tweeters/Kusama enthusiasts, always replying with additional commands that they could try, and created a sense of involvement regardless of, say, the number of miles between Pittsburgh and London!
For those at Tate Modern, the experience was far more insightful; not only did they get to see an amazing Kusama exhibition but they were in physical proximity of The Hello Cube! Besides being able to view the installation's constantly changing interior dynamics that were projected onto an adjacent wall, visitors could also interact with The Hello Cube by saying their hellos or anything else they thought fit to share with the cube (besides tweets, it was programmed to respond to external stimuli such as sound or voices).Visitors could even place their hands inside the cube and see their arm reflected unto infinity!

Hellicar and Lewis, the creators of The Hello Cube, describe it as “an installation that exists as a sculptural object that you can look inside, see patterns, and an infinity of reflections.” It takes inspiration from Kusama’s work titled The Passing Winter, but as noted by its creators, it differs from Kusama’s work in that it is capable of responding to people and to its environment.
The work of Hellicar and Lewis has been featured at The Creators Project and the duo are “interested in creating groundbreaking experiences that use art, technology and design to take people into the moment and impart lasting memories.” In an interview, they noted how they had undertaken a similar project in the past called The Hello Wall, a dynamic outdoor installation where users could control the projections on an external wall in Wembley by tweeting at it.
While Hellicar and Lewis have used Twitter's real time capabilities to foster a dynamic perpetuity and engagement that is both brilliant and unprecedented, the creation of Twitter personas for artworks in itself is intriguing. On Twitter, the inanimate, the intangible, and even the immortal can all lay claim to accounts; San Francisco’s Fog, the Bronx Zoo Cobra, and Voldemort are all suspiciously active! So why can’t art transcend notions of the self, at least on social media? Thus, not only was The Hello Cube an incredibly interactive installation, but its presence on Twitter essentially transformed it into an anthropomorphic object, increasing its accessibility in both a literal and psychological sense.

It would surely make an interesting experiment to see how people interacted with a painting were it to have a twitter account. Wouldn't it be fun if museums created Twitter personas around special exhibitions? What would Rembrandt tweet? How about an account for Abstract Expressionism? Of course, these accounts may have to be temporary but a lot could be learned in a series of short bytes of information. One sees a considerably twitterable future.
For now, we have the delightful The Hello Cube, which having been removed from the Tate, bade farewell to its visitors and declared that it was ‘time for a cube to enjoy the sunshine...” Of late, it was tweeted that The Hello Cube will once again start taking commands this Friday, but as the installation politely requests: "Just don't forget to say Hello!"
Engaging Technology: uCurate and uExplore at the Clark
What’s going on at the Sterling and Francine Clark Institute in Williamstown, Massachusetts? Let’s see, there are iPads, tablets, interactive digital programs, touchscreens and kiosks throughout the galleries, the new exhibition, Clark Remix, and oh yes, new curators- YOU.
In a February press release, the Clark announced its exciting new initiative to encourage visitor interaction and participation in its galleries. According to the press release, Clark Remix is "a dynamic salon-style installation featuring some 80 paintings, 20 sculptures, and 300 of the institute’s finest examples of decorative arts."
programs, touchscreens and kiosks throughout the galleries, the new exhibition, Clark Remix, and oh yes, new curators- YOU.
In a February press release, the Clark announced its exciting new initiative to encourage visitor interaction and participation in its galleries. According to the press release, Clark Remix is "a dynamic salon-style installation featuring some 80 paintings, 20 sculptures, and 300 of the institute’s finest examples of decorative arts."
As part of the exhibit, the Clark has introduced the interactive, digital programs uExplore and uCurate. Both programs are accessible online, on the visitor’s own personal device, on touchscreens and kiosks throughout the gallery and on iPads and tablets provided by the Clark for use in the museum. Basically, the programs are EXTREMELY accessible and user friendly- I myself have spent all afternoon here in Pittsburgh exploring the Clark’s collection and building my own exhibition, instead of reading for class (ahh priorities).
The Director of the Clark, Michael Conforti explains the premise of Clark Remix,
Clark Remix represents one of many programs that the Clark is developing to engage audiences in exciting ways. Clark Remix allows us to present our permanent collection in an installation that is both beautiful and innovative. Our salon-style presentation provides a very different and intriguing perspective on many of the works that have become familiar favorites for Clark visitors. Adding virtual components to the exhibition allows us to reach new audiences and invite them to discover and interact with our collection.
It works like this. uExplore allows the visitor to learn more about the Clark’s collection in a visually stimulating, highly organized, and digitally oriented way. Items are grouped into categories (paintings, sculpture, glass silver and ceramics) to allow the user to navigate with ease through the extensive collection. Selecting an image of the desired object, a more detailed, but not overwhelming, explanation of the item becomes available. When appropriate, audio and video clips accompany the information.
It is a beautifully designed and easily navigable interface. uExplore’s presence in the gallery encourages visitors to delve more deeply into the history of the collection, while they are on-site.
The second digital application to accompany the exhibit, uCurate, gives visitors the opportunity to participate in the curatorial process. As the name implies, YOU, aka the visitor, plan and design a 3D virtual exhibition with the Clark’s collection. The participant makes all decisions, from what to include and how to arrange
the objects, to wall color selection and wall text. Users of the program have the option to submit their designs for consideration by Clark’s curatorial team AND to share their designs through social media channels (promoting the museum and the digital program). Submissions to the Clark will be reviewed regularly. Why submit your design for professional review by Clark curators? Because if selected, the virtual design will be transformed into an actual exhibition! The lucky designers will be invited to assist in their exhibition’s installation, in the decision-making process, in the creation of wall text and in writing the curator’s statement.
uCurate and uExplore were designed by the Clark in collaboration with Swim Design Consultants and Virtual Gallerie to afford the public a voice and role in the museum’s exhibition planning process. Allowing the public to suggest actual designs for implementation challenges what has been the accepted and traditional decision-making process in the museum. That is, all decisions are made internally; the public only receives, not contributes. But the Clark is trying something different. In a recent New York Times' article on the Clark’s innovative crowd-sourcing approach, Conforti said,
For generations, curators ran the show and told you what to believe. In a world of blogging and Wikipedia, we realized that we can learn from our audience, and from multiple interpretations.
This is Museum 2.0 in action. Where visitors become users and museums become, as Nina Simon explains, “dynamic platforms for content generation and sharing.”
for content generation and sharing.”
So Kudos to you, Clark Museum. This is an engaging and relevant use of technology where the user AND museum win.
PIPS:lab Diespace, Interactive Multimedia Experience
PIPS:lab recently made its US debut during a festival featuring Dutch artists here in Pittsburgh. The Amsterdam group has been performing together for about a dozen years. The work that they performed was categorized as absurdist media theater and was a short evening length work without intermission. The use of technology for this performing group is integral. The performance itself was noteworthy for its innovation on a number of different levels. It is worth noting, however, the problems that PIPS:lab had in functionally executing the performance due to glitchy technology. The performance, Diespace, was essentially an introduction to a fictional new social network site that audience members were encouraged to visit after they die (or die in order to visit). The actors polled the audience about their opinions regarding whether or not there is life after (or before, humorously) death. These polls were conducted with a cool audience participation tool of light capture setup where the audience essentially wrote on a screen upstage.
The other insertion of tech into the performance involved video/audio remixes of various clips taken of audience member during and before the show. These clips were then edited in real time into the performance. This, in turn, served to engage the audience but through a pretty controlled format. The display of the video and audio taken from the audience drew laughter and made the audience excited and was a high point of the performance lending to greater investment from the collective. Additional audience participate was to be had through a lottery during the show where the faces of the audience were put into a virtual tumbler on the screen upstage. Three audience members won prizes with the grand prize being a premium account for Diespace (which included significant stage time for the audience member who won it).

The performance unfolded at a relatively brisk pace with musical interludes to cover moments where the technology and content was being prepped. The problem with this was that the performers ended up being a bit un-invested in the music and as a result it was hard to be carried away by the performance. It was easy to check out during these scenes through the distractions on stage. It was the sense of this reviewer that there was only one true musician on stage, a fact that was born out by the program notes about the artists backgrounds.
At least three times during the performance there were loud warnings of a computer crash each time forcing the performers on stage to repeat a few moments to a few minutes of the action. This in turn lent to a stutter stop feel to the performance. Execution of Diespace did not look like it was easy and to be certain what PIPS:lab is trying to do is not easy in general. They deserve applause for attempting to stitch together so many constituent elements in the moment. It was fascinating at times to see the failures of the technology and there was rarely a moment where the audience did not have something that they could try to be engaged in. The relative successes and failures of this performance reinforce the point that some technologies have a ways to go before they are both accessible to independent performing artists.
The innovation of groups like PIPS:lab hopefully will be the wave of the future and it is gratifying to see media artists take the stage with musicians and actors. The combination of talents of stage was a rich soup and Diespace was a valuable experience for the insights that it gave with regards to generation of true multi-disciplinary live work.