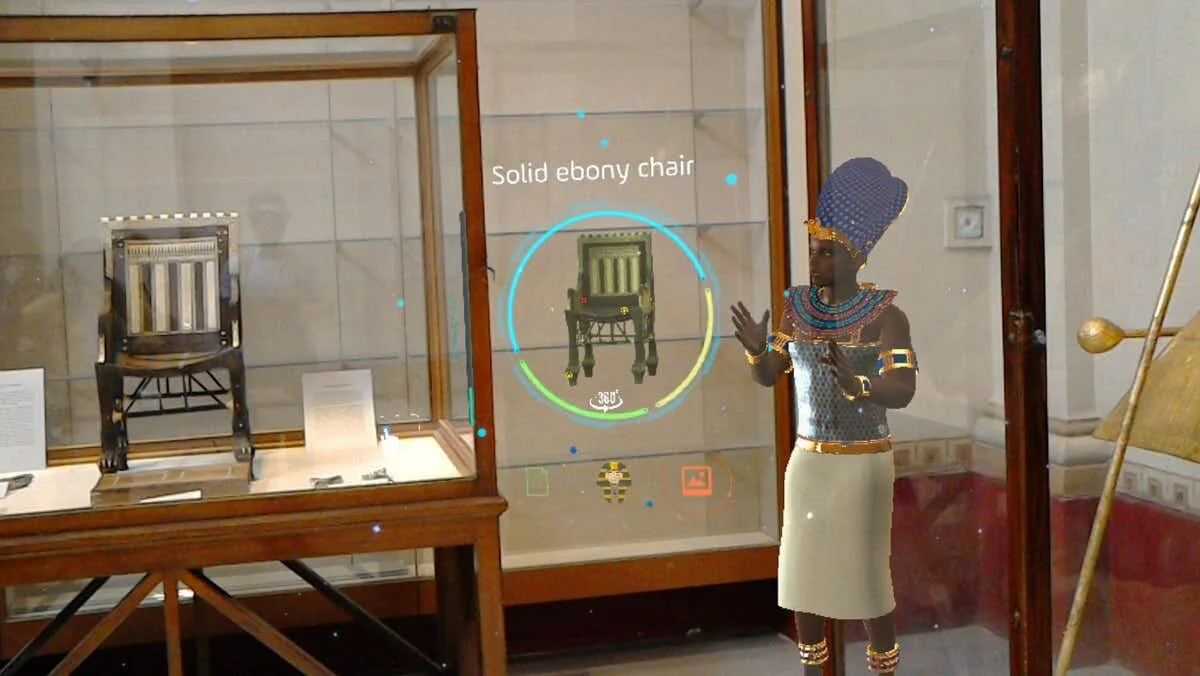
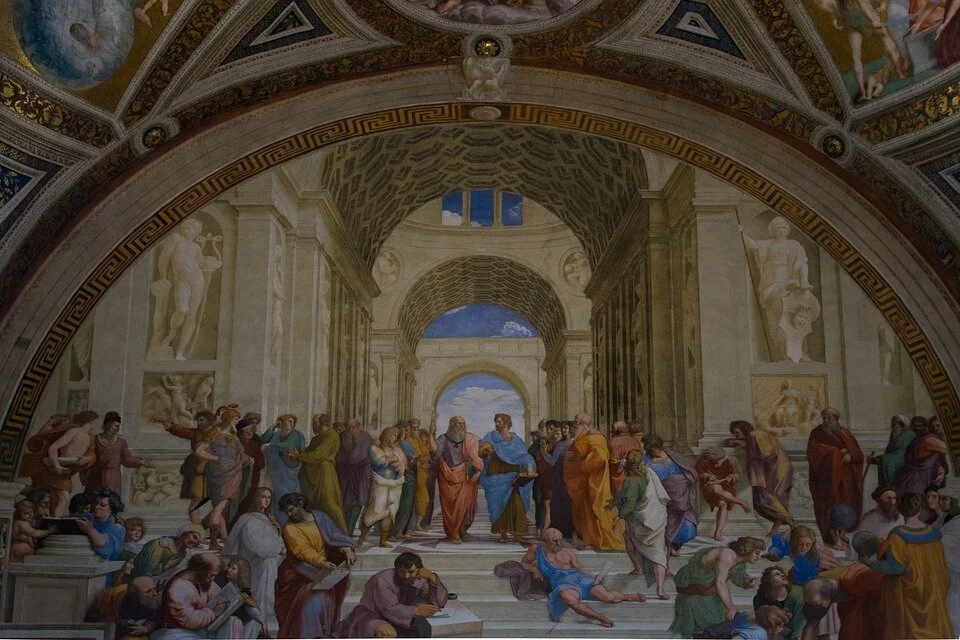
As museums and heritage attractions are restricted by distancing and capacity rule during the COVID-19 pandemic, digital strategies undoubtedly gather more interest than ever before. Virtual Reality (VR) has been put to use in the cultural sector a way to deliver exciting and immersive exhibitions. The communication between archaeologists and technicians is critical for the accuracy of the VR reconstruction and museums should work closely with their technology team and emphasize their obligation to public education in these creations. This insures that museums can keep the integrity of cultural heritage exhibits while providing an exciting and immersive educational experience of the past with technology that looks toward the future.
Living in a Deepfake World
Deepfakes, or AI-generated synthetic media, are becoming increasingly prominent in the digital age and are being used across industries more frequently than ever before. Unlike common uses of AI that modify existing media given, AI that generate Deepfakes attempt to simulate that media, often using an individual’s likeness as a source of AI learning. Deepfakes can be a fun experiment for swapping faces, but they present a wide variety of malicious uses that has permanently altered the trust and engagement of media. Thus, society must continue to challenge the validity of sources and find new ways to protect media and the truth.
What is MR and How Does it Create Exceptionally Immersive Experiences?
MR, or Mixed Reality, is appearing across the arts world, but its actual meaning is not well understood. A strong beginning includes a foundational understanding of the concepts of reality and virtuality. The future application of MR technology is unlimited, increasing the possibility of creating experiences that reflect what is seen in sci-fi films. While many practitioners believe that MR is the future, the technology lacks popularity in the consumer market. However, with the continuous development of MR technology, more cost-effective solutions will be found, and the future of a truly immersive experience will come.
Bringing Stories to Life: How Pixar Accomplishes Realistic Animation
Pixar revolutionized the animation industry through innovative technology and incredible storytelling. It was responsible for core developments in computer graphics history, blending technology and arts to make many of their films possible, leading to its massive success. 3D computer modeling technology has not only allowed for more efficient and faster animating, but it has opened the door for more people who are interested in joining the industry. It now easier than ever to download these softwares and begin learning how to animate. For artists in industry, there is not longer a limitation in the art that is waiting to be created – their visions can become a reality with the continual development of advanced animation technology.
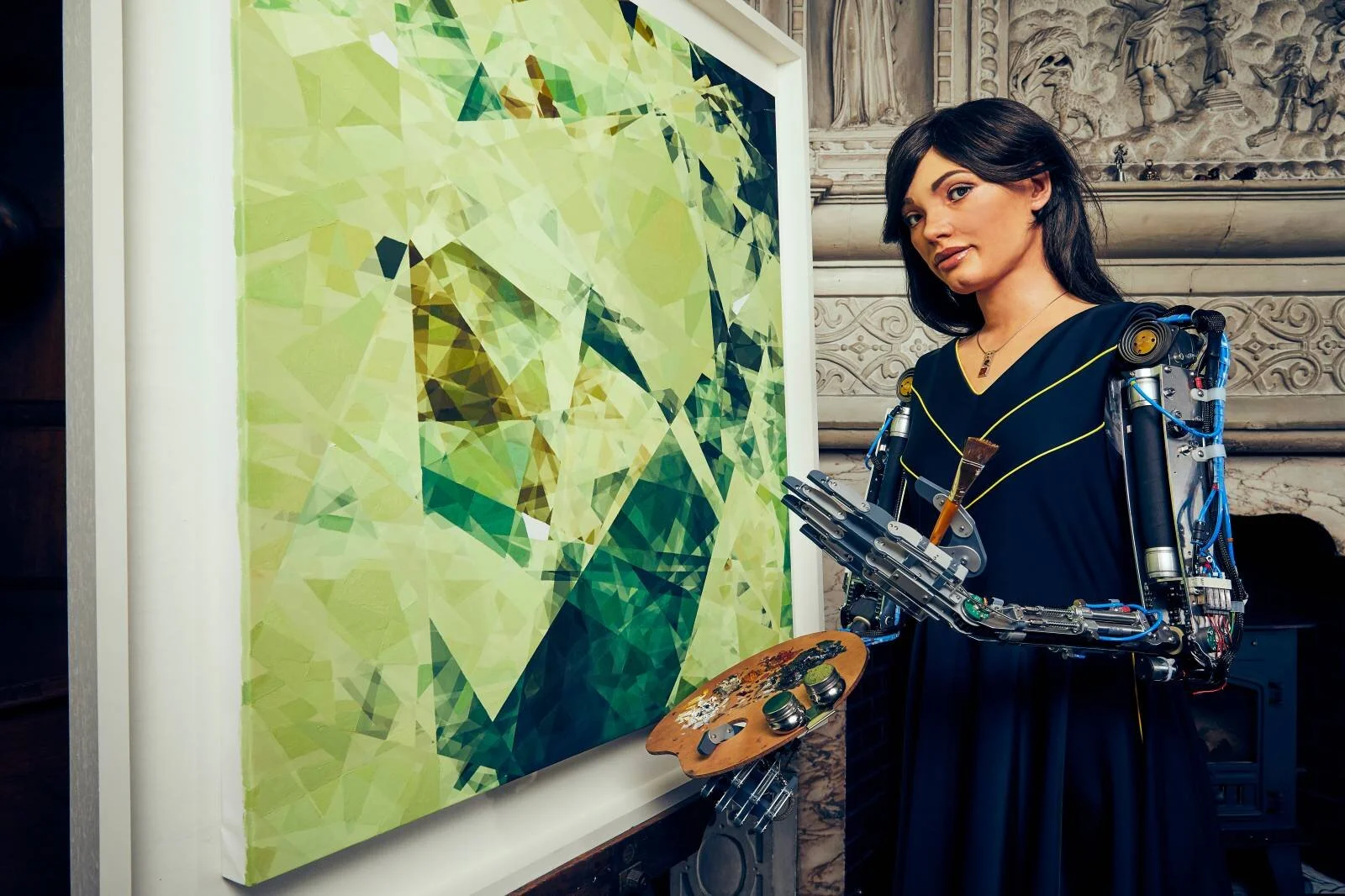
Could It Be Sentience or Just Expert Coding? The Emerging Role of Robots in the Arts
Few innovations represent the intersection of humanity and technology more famously than that of the robot. Like art, robots are the result of humanity’s urge to create something new in its own image – and, also like art, they have become an inescapable part of our world. In a post-pandemic world whose inhabitants have become accustomed to virtual experiences, these robotic arts roles, including facilitating virtual museum visits, performing through a computer program rather than a script, and creating what maybe approaching original and creative art, are probably here to stay.
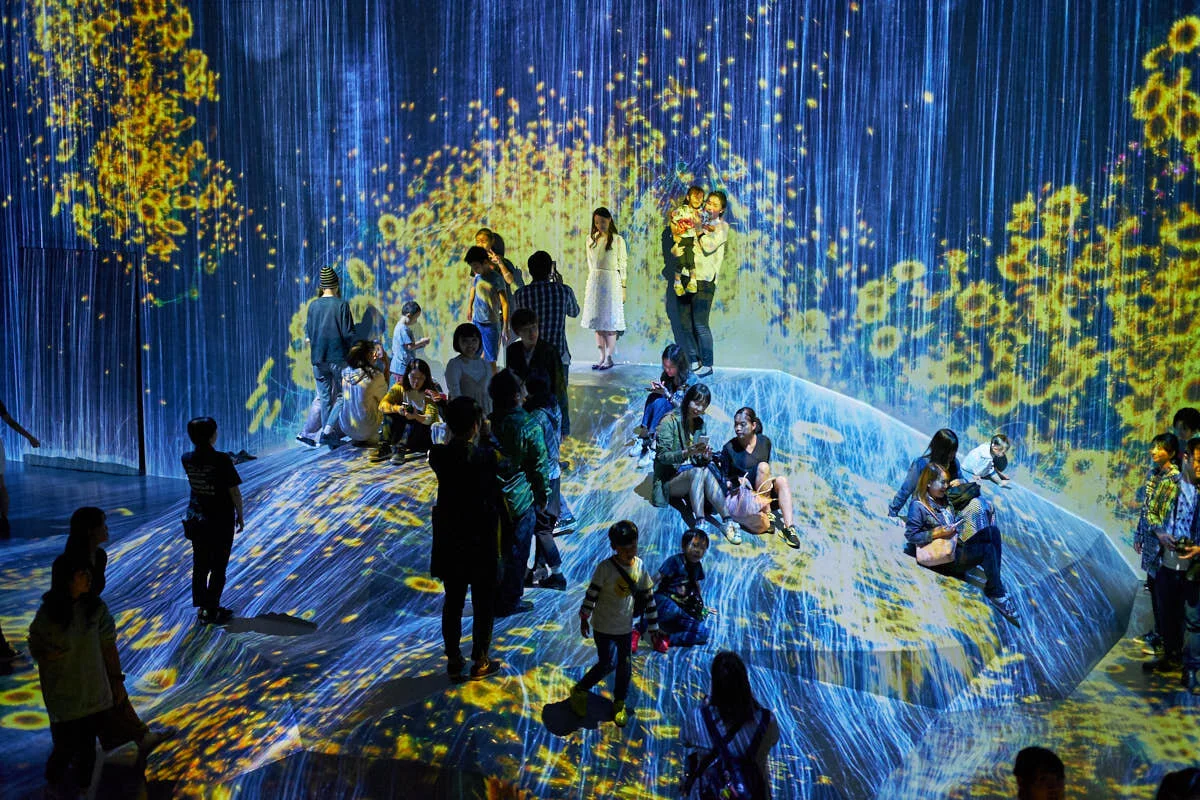
Artistic Futures: Digital Interactive Installations
The concept of interactivity in the artistic field became popular in the 1950s due to the realization that interactive art could serve as a bridge between connecting artists and audiences in new ways. More importantly, audiences were able to become part of the artwork through their expression in experiencing the artistic process. These advances have led to greater accessibility in individuals’ artistic experiences. Moreover, the physical return to museums and galleries post-covid enhances digital interactive installations since audiences can experience this art live in a physical space, fostering a new sense of curiosity and community. The more frequent implementation of digital interactive installations in the technological age is just the beginning of its artistic evolution. The digital world of art is a hub of creativity and eager exploration, paving the way for a bright and innovative future for a fairly new form of art.
Exploring Accessible Technology in Theatre: Captioning
According to the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders, one in eight people in the United States ages 12+ have hearing loss in both ears. Given the prevalence of hearing loss in the United States, it is in performing arts’ organizations best interest to include solutions to make their work as accessible as possible. Disability advocates have spoken out about the need for better accessibility in the arts. No matter the medium captionins is provided, whether looking off stage, at a handheld device, or directly through the lenes of AR-supported glasses, all techonolgies are ensure that the theatre is a welcoming place for all.
Business Intelligence & Analytics in the Arts
The idea of collecting data is not new within the nonprofit world. Today, community-facing nonprofits are realizing how critical data collection is in achieving and reporting on their missions. According to the most recent edition of Salesforce’s Nonprofit Trends Report, organizations that ranked higher for digital maturity, or their ability to leverage data to inform decision-making, had a greater likelihood of exceeding goals during (and after) the COVID-19 pandemic. As more user-friendly technology are applied in CRM systems, the obstacles of domain knowledge are diminishing. This results in a positive implication of what these systems can do for nonprofits and how it can transform how these organizations are run. However, the lack of budget and training resources makes the obtention of these systems unlikely for many nonprofit organizations.
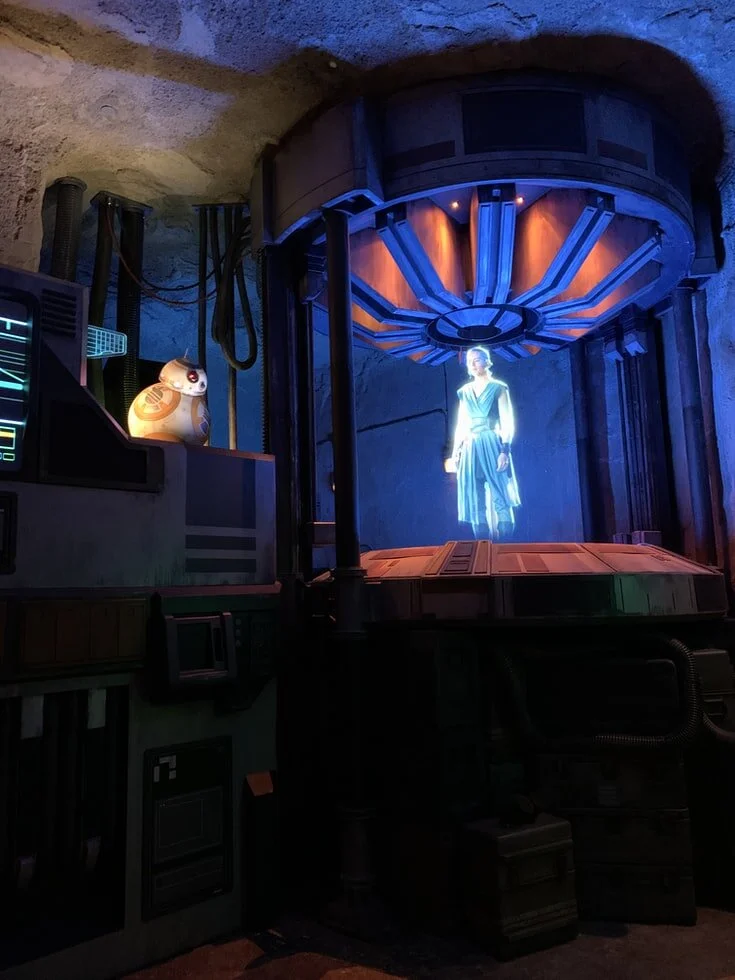
Holograms: Where Physics & Art Collide
“Help me Obi-Wan Kenobi. You’re my only hope.” The iconic opening scenes from the original Star Wars film, A New Hope, epitomize what we think of when we consider the word “hologram.” In the minds of science fiction fans everywhere, the hologram is a concept that evokes feelings of wonder at the possibilities for technological advances. Whether someone is a fan of science fiction or not, it can be agreed that holograms have had a distinct impact on the arts. Although they were not initially intended for anything other than scientific use, holograms made their way into the public’s imagination and conjured up ideas of the future of technological advances.
Aristotle & Gaming Case Studies (Tragedy is Fun: Aristotle Revisited)
As noted in How Video Games Can Serve as an Engagement Experience, video games, particularly RPGs, are widely popular and engaging with exceptional character and plot structure. The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim and The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt exemplify Aristotle’s model of dramatic tragedy in a modern form. These case studies prove that video games are fun, tragedy is fun, and by marrying the two, arts organizations can experiment with exciting new forms of audience engagement!
How Video Games Can Serve as an Engagement Experience
The expansion of technology has enabled a wide array artistic growth in innumerable forms - often taking a life or genre of its own. One artistic form that has dominated the market since technology has become common in society is video games. The materials below serve as introductory infographics for arts organizations, detailing core considerations and a streamlined video game planning process. Additionally, it lists common employees needed to conduct video game production, common engines and coding languages used and their learning difficulty levels, so that arts organizations can jumpstart their gaming creations of their already-mastered craft.
NFTs Legal Considerations and Implications
In early 2021, the $69M sale of Everydays – The First 100 days, by Beeple, sprung NFTs from a niche but growing section of the digital art world into the mainstream public consciousness. Google searches for NFTs skyrocketed. Saturday Night Live spoofed the rapid sector growth with a parody of Emenim’s “Without Me” entitled “What the Hell’s an NFT.” A 10 second clip of the sketch was subsequently turned into an NFT which sold for $365,000. As pop culture awoke to and embraced this facet of the digital art world, so too has the urgency for artists, museums, and collectors to understand the rapidly evolving legal considerations within the NFT space.
Welcome to the 2021-2022 Year of AMT Lab!
We are busy kicking it back into high gear here at the Arts Management & Technology Laboratory, and I hope that you’ve enjoyed the steady stream of our summer content! My name is Liz, and I am thrilled to be taking on the role as Chief Editor of Research for 2021-2022. Lutie Rodriguez, last year’s Chief Editor, focused on the intersection of arts, technology, and policy, in addition to the ever-changing realities of the global pandemic. This year, we will investigate how arts organizations are using technology to adapt through Covid-19, as well as topics such as Climate Justice, Big Tech, Gaming, and the always-fascinating subjects of Blockchain and NFTs.
Positive Implications of Deepfake Technology in the Arts and Culture
Deepfakes, one of the hottest topics to burst onto the technology scene in the last five years, have received a lot of negative publicity because of the risks they can present in the hands of bad actors. However, when used in good faith, they have many positive and exciting uses within the arts and culture sector. This report will briefly explain what deepfakes are and how they work, as well as some of their weaknesses and negative implications. Additionally, three case studies will examine the positive ways in which deepfakes can be used in artistic and cultural institutions.
Using Augmented Reality in Classical Music
How can the visual technology of augmented reality be used to enhance audience engagement with classical music and in the music industry as a whole? In the arts realm, AR has been used in both the classical music and popular music realms to cultivate audience engagement with visual components to the listening experience. This article provides an overview of AR as a technology and its usage in the music industry.
How Streaming Services Use Algorithms
The Streaming Wars in 2021: Netflix, HBO Max, and Disney+
Streaming services have won the battle over the box, and now the streaming war is in full gear. Netflix, HBO Max, and Disney+ have taken differing approaches to capturing a competitive advantage to be the top streaming service users turn to. Read about where they stand in this research by Helen Hejran.
How VR and AR are Changing the World of Immersive Theater
In the ever-changing and technologically advanced age that we are currently in, there are integrations of new technologies into our lives almost everyday, and the arts are no exception. The world of theater, especially that of immersive theater, has been experiencing a technological revolution of its own thanks to advancements in and the adoption of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). Contributor Amelia Stevens explores this in her research.
NFTs and Arts Management
As the world seemed to erupt with NFTs in spring 2021, AMT Lab thought it would be an appropriate time to curate a collection of essays on the emerging, some might say exploding, world of NFTs with a focus on the arts and technology’s disruptions. The following article provides context to the arts marketplace, ownership, and the disruptions caused by blockchain technology, especially NFTs, and concludes with a short commentary on the forthcoming collection and an existential thought to send you along your way down the rabbit hole of NFTs and blockchain.