Arts organizations play important roles in their communities beyond providing access to art itself. Arts organizations are also valued venues for human connection. In LaPlaca Cohen’s Culture Track 2017, 68% of respondents indicated “interacting with others” as a draw for cultural participation, and about half of respondents in LaPlaca Cohen’s 2020 study, Culture and Community in a Time of Crisis, revealed desires for cultural organizations to communities “stay connected” during this time. These data points demonstrate that audiences look to arts organizations to not only foster connections through art, but also nurture communities beyond the art. One way to do this is by creating virtual third places. While arts organizations are unlikely to build entire VR-based worlds for their patrons, arts administrators might consider how to adapt existing platforms to help reproduce some if not all of the socially-leveling, conversation-focused environments they’ve worked to cultivate in their physical spaces.
Adapting to the Pandemic: The Enterprise Center and Wolf Trap
To investigate how the Covid-19 pandemic is affecting the live music industry, we will look to case studies of venues that normally host concerts. In this first set of case studies, we will look at the Enterprise Center and the Wolf Trap Foundation for the Performing Arts. The Enterprise Center is a 22,000 capacity (for concerts) arena in St. Louis, Missouri. Located in Northern Virginia, Wolf Trap Foundation for the Performing Arts was the first National Park dedicated to the performing arts. Performances take place at the Filene Center, The Barns, and Children’s Theatre-in-the-Woods, and the foundation also operates the Wolf Trap Opera Company. Because it is currently not safe for either of these venues to operate at full capacity, these case studies will investigate technology-based alternatives.
Opportunity or Challenge? Artificial Intelligence for Museum Audience Engagement
To improve museum operations, museum management is increasingly taking advantage of artificial intelligence (AI) technology to understand their collection data, their visitors, and their exhibitions. Audience engagement is one of the most significant factors that museums need to consider in their operations: it is an implicit element that connects people to collections and should be achieved based on a deep understanding of visitors, collections, and exhibitions. Within the past few years, AI technologies have shown their potential to bring previously inaccessible insights to museums based in three main areas: machine learning, chatbots, and neural networks.
What Arts Organizations Can Learn From Sports: The NBA
This week, AMT Lab has been investigating what lessons arts organizations can learn from sports as they seek to provide engaging digital experiences for audiences. The National Basketball Association (NBA) is the most prestigious and well-known basketball league in the world, making it imperative that they continue to engage their fans during the pandemic while securing revenue from broadcasts. They found solutions that would permit fans, specifically younger generations, to continue to interact with each other during the games—something that arts organizations could apply to their virtual performances.
What Arts Organizations Can Learn From Sports: La Liga
As arts organizations look to provide digital experiences to engage audiences, there are lessons to be learned from sports leagues that have restarted seasons and successfully broadcast them to international audiences amidst the Covid-19 pandemic. One example is La Liga. The Spanish league most commonly known as La Liga is one of Europe’s top five soccer leagues. The 2019-2020 season kicked off on August 16, 2019 and was set to go until May 2020, but as the world—and Spain specifically—saw the rapid growth of Covid-19, the league was temporarily suspended. With the campaign entitled #BackToWin, it was the second major European league to resume, with no fans in the stadium and strict safety guidelines. To make the matches a marketable product from an entertainment standpoint, broadcasters experimented with AR “fans” and artificial crowd noise. A spike in La Liga’s international viewership reflects not only the fans’ desire for the return of live sports, but also the value of the product La Liga and its broadcasters were able to create. As sports—and the arts—look for ways to perform virtually, La Liga offers an example for how to do so successfully.
What Arts Organizations Can Learn From Sports in the New Normal
So why sports? Although the general perception of the sports industry focuses on teams and their players, the sports industry encompasses a vast number of stakeholders that affect the state of the industry. The industry is made up of a complex web of live sporting events, food stands, media rights, and brand sponsorships. Most importantly, as with the arts, fans and audiences play a key role when it comes to analyzing the state of the industry. Unlike the situation for arts audiences, the global sports market is growing and expected to continue to grow due to esports, an increase in the number of internet accessible devices and the advent of 5G. What opportunities could this offer arts organizations looking for digital innovations to reach audiences?
Young, Diverse, and Loyal: Engaging a New Audience
Many institutions are rethinking their approach to diversity in the light of renewed protests in support of the Black Lives Matter movement. Theatre companies throughout the nation are a part of this wave, rethinking everything from season planning to staff structure. Yet one of the largest issues at hand is the lack of diversity in audiences. Theatre audiences are dwindling, and those audience members that remain tend to fall into a very narrow set of demographics: usually older, white, and affluent. Theatre companies will have to reach out to new groups If they want to continue working and thriving well into the future.
Build Interactivity into Public Art: Technology Interventions
One key element that differs public art from art produced for display in museums and galleries is that public art is often site-specific. It is critical to make public art more reflective of the place and community in which it resides through interactive and participatory approaches. How can technology contribute to the systems and interventions designed to drive public engagement?
Digital Network Strategies for Nonprofits
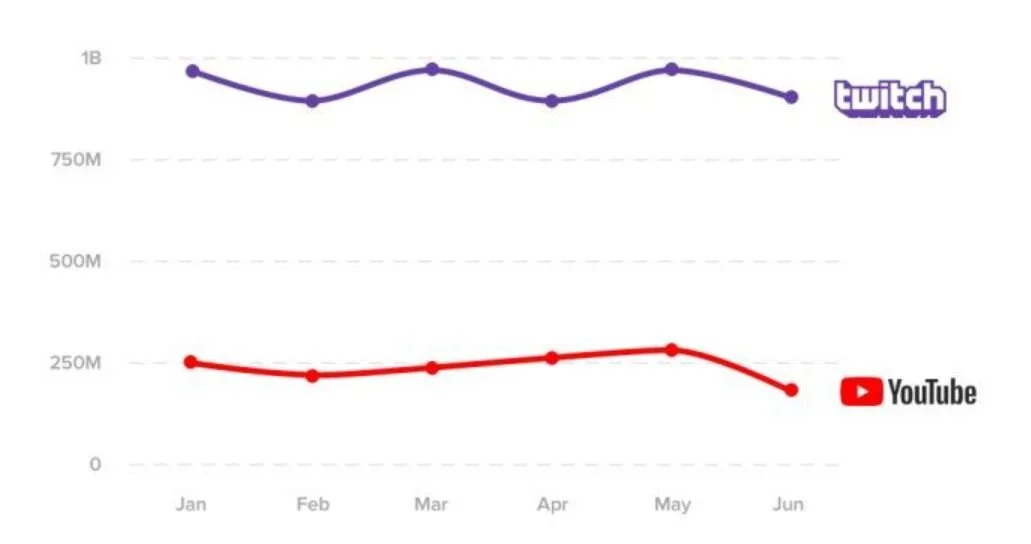
This article will look at three companies, an established ‘big fish’ company, a late entrant to the market, and a ‘blue ocean’ company. Blue Ocean refers to the idea that a new marketplace with untapped potential can exist between two common marketplaces and one can create their own supply and demand. The companies this article will look at are; Twitch.tv, Mixer.tv, and Voxpop Games.
Building Interactivity into Public Art
Do you think that interactivity can improve an audience’s relationship with public art? One key element that differs public art from art produced for display in museums and galleries is that public art is often site-specific, meaning it is created in response to the place and community in which it resides. Therefore, creating public art needs a certain level of customization to the physical local environment.