The demand for STEM practitioners is growing in tandem with the demand for workers who are equipped to think about their social and ethical aspects. The intrinsic values of the arts, such as empathy, community, and imagination, combined with the logic of the STEM model, create a more well-rounded experience for youth. Agnes Chaves, a new media artist and founder of STEMarts Lab, advocates for the idea that STEAM education practices allow students to understand the ethics behind new technologies and their impact on nature and humanity when approaching a problem. Particularly for larger societal problems such as digital inequity, it’s crucial that students perceive themselves as caretakers of the planet and global citizens.
TBT: Education, Gamification, & Public Policy
Haptic Feedback: Feeling the Dance You Cannot See
Dance relies on the audience’s sense of sight to experience a performance. However, dancing itself is a very tactile experience. A dancer’s precise movements depend on a heightened internal awareness of the body – how joints are stacked and what muscles are activated. They must also maintain an awareness of external forces – how one limb moves in relation to the other, how their skin feels sliding against the floor, and where they sense other dancers moving with them in space.
The experience of the audience is vastly different from that of the dancer. Is there a way to bridge this divide and communicate a multi-sensory experience to the audience, and allow those who cannot see to feel? Tapping into this sense of touch might help audiences experience dance in a new way.
Open Access and Why it Matters in the Museum Space
Amidst Covid-19, many museums moved to sharing collections and exhibitions virtually. However, even before Covid, museums began sharing their collections in a virtual, accessible manner with Open Access. It is estimated that nearly 1,000 cultural heritage institutions world-wide have published some or all of their collections with Open Access usage. While Open Access exists in other industries, such as in libraries, this article focuses on the context of Open Access in the museum space.
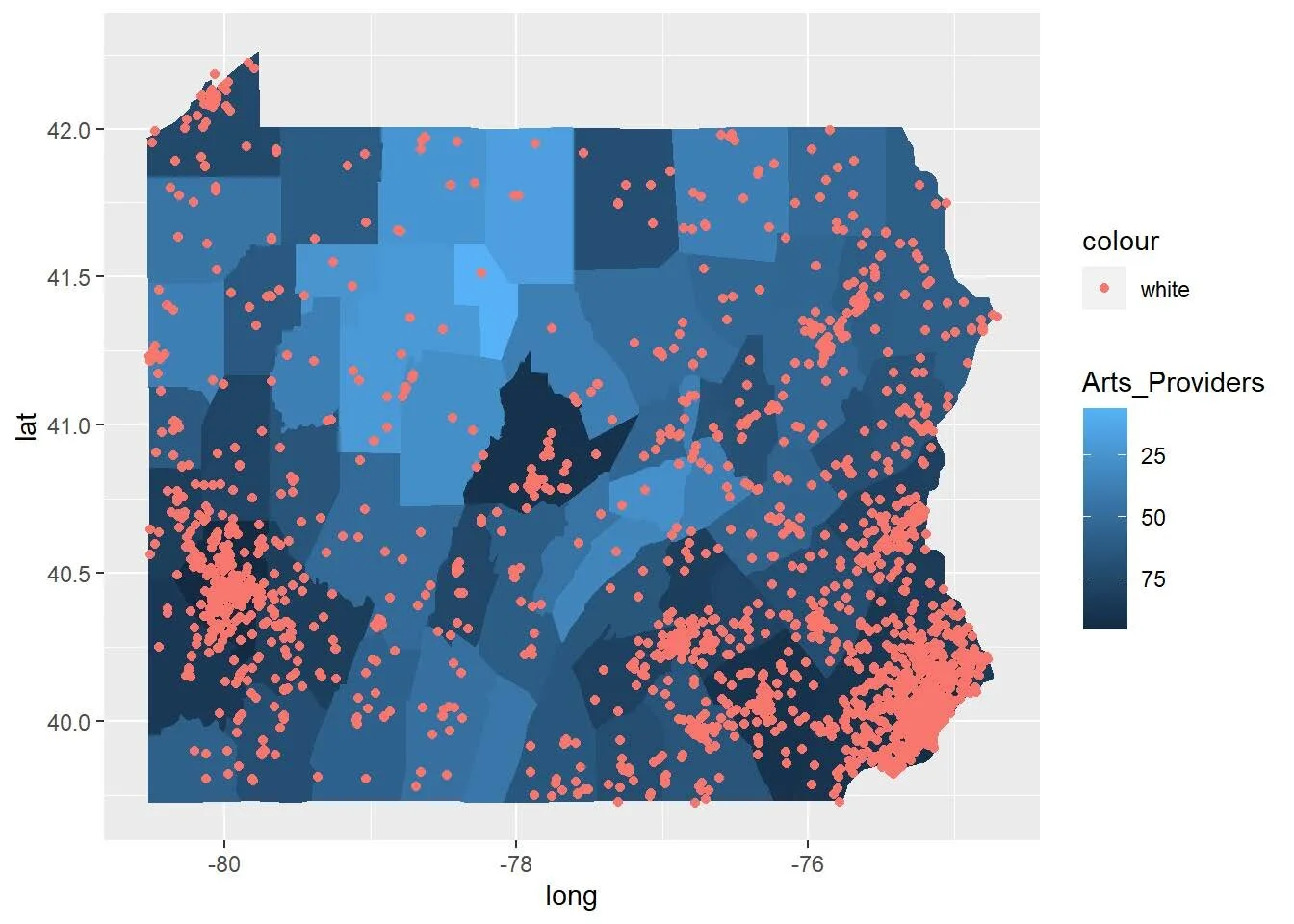
Arts Vibrancy and Digital Access: Part 2
Part one of this research looked at the relationship between broadband deployment and arts vibrancy in the United States, focusing on Texas. This article examines factors that are driving the digital divide and relatively low arts vibrancy in two counties on the Texas-Mexico border and how that could inform policies in the United States as a whole.
Part 2: Digital Access and Arts Vibrancy
Access to the arts is not even across the United States. The ways that people living in rural areas access artistic content differs from how people participate in urban centers. Additionally, as the sector is beginning to grapple with, access to the arts varies across racial and ethnic groups. Comparing county-level arts vibrancy data is one way to detect these patterns. While the number of dollars put into the arts in the form of compensation and expenses seems to be the best predictor of overall arts vibrancy, implementing municipal WiFi appears to be an opportunity for growth since analysis indicates that it can increase arts vibrancy.
Digital Inequity in the Arts: Part 1
The coronavirus pandemic has changed everything we assumed about the world. Everything that once seemed impossible to ask for in terms of public policy is now possible, including rent suspension, eviction moratoriums, and universal basic income. But, it has also revealed inequities, including who has access to the arts. This project, published in two parts, evaluates racial equity through the lens of the arts sector during the Covid-19 pandemic by asking the questions: who has access to the arts and, fundamentally, what does access look like?
#TBT: Accessibility in the Arts
This past year, contributor Kate Tsai gave us several fantastic articles about accommodating disabilities for arts non-profits. It really seemed to interest our readers so we wanted to re-post some of the Kate's best articles, and remind our audience of a few past gems as well.
First Kate gave us a fantastic infographic about many different types of impairments and disabilities that can create barriers when interacting with an arts organization. In addition, she walked us through 6 quick ways to adjust websites, making them more readable and clear for audiences of all kinds.
Some of our most well-read accessibility articles center on technology for museums. In the spirit of other brief overviews. In 2016, contributor Christine Nolan showed audiences just which technologies can contribute to a more accessible and audience-friendly museum experience.
5 Technologies with the Potential to Enhance the Museum Experience
In the same vein, contributor Stephanie Sun wrote about 5 technologies that give audiences ways to connect differently with the arts experience. Although these weren't highlighted directly as opportunities to improve accessibility in Museums, they are all opportunities in these areas. For instance, 3-D scanning has made it possible for Museums to create touchable replicas for people with vision impairment. What are some other applications of these technologies that open doors for improved accessibility.
Opening Doors
Museums are not the only ones looking to accommodate a wider range of audiences. Contributor Christine Sajewski writes a two-part piece on what sensory-friendly performances are and how they are implemented effectively in the field. The first part focuses on the 'what' and the second part focuses on the 'how'.
Building Accessibility with New Tools
Learning Disabilities: What Arts Managers Need to Know
From Six Degrees of Separation to Art.sy
 Whether your goal is to start an art collection, expand your collection, discover a new artist, or simply to keep up with everything there is to know about your friends on Facebook, the soon-to-go-live startup website Art.sy is worth a look.
So you want to be an art collector? You have been thinking about purchasing your first piece of artwork (and I do not mean the Starry Night print you purchased from poster.com…), but you do not know where, when, why, how much, what, or how to proceed. Maybe you are a veteran collector, for profit or not, and are looking to expand your collection. Let Art.sy do the work for you.
Whether your goal is to start an art collection, expand your collection, discover a new artist, or simply to keep up with everything there is to know about your friends on Facebook, the soon-to-go-live startup website Art.sy is worth a look.
So you want to be an art collector? You have been thinking about purchasing your first piece of artwork (and I do not mean the Starry Night print you purchased from poster.com…), but you do not know where, when, why, how much, what, or how to proceed. Maybe you are a veteran collector, for profit or not, and are looking to expand your collection. Let Art.sy do the work for you.
Created by Carter Cleveland, a Princeton University computer science engineer, and backed by a handful of today’s most influential players in the social media, fine arts, and technology industries, Art.sy is the newest and potentially most powerful addition to a collector’s and artist’s networking toolkit. Don’t believe me? Maybe you’ll believe some of its investors and advisers including the CEO of Google, Eric Schmidt, Twitter creator, Jack Dorsey, the owner of Gagosian Gallaries, Larry Gagosian, former executive at Christie’s Auction House, Sebastian Cwilich, and the CEO of Pandora, Joe Kennedy, just to name a few. If you are a new, online startup, it is safe to say THOSE are the names you want associated with your project. So now that we have established just how popular Art.sy is among the big wigs in the industry, let’s figure out why.
If you have ever used Pandora to search for a song or musician, you are already familiar with “genome technology” and how Art.sy will perform. What differentiates Art.sy from the rest is the Art Genome Project. A simple search for a painting will return not just the desired title, but additional works of art related to the original search recommended for you by yours truly, Art.sy. Each work in the collection is classified by various characteristics such as asking price, genre, theme, colors, period and “ism” to connect it with other paintings in the database. A search for one painting will generate a list of paintings that share similar classifications, exposing users to artists and paintings they may not have been familiar with. Linking with Facebook and Twitter, Art.sy users can share their searches and discoveries with others, educating a wider audience and strengthening the presence of art online.
For example, a search for Max Ernst’s surrealist painting The Couple in Lace would return not only the painting itself, but information on Ernst, the painting, its location, paintings of other Dadaists and Surrealists, paintings of couples by other artists, and paintings whose creators were influenced by the work and style of Ernst. Note well, Art.sy is geared more toward lesser-known and on-the-rise artists (sorry, Ernst) because its users are likely to be beginner collectors with smaller price ranges.
For each work of art, Art.sy will provide the specifics for contacting the gallery or the artist (where possible) to begin a conversation and facilitate a purchase. Making collectors of those who previously could not or did not know where to begin is just the beginning of what Art.sy has to offer us.
Since its initial launch last November, hype has only grown. The collection itself is still in development and has yet to go live, but you can visit its website to register for your official invitation to join what could be the most extravagantly marketed and led, online network making fine art accessible to the masses. Will you RVSP?