In 2021, TikTok updated its privacy policy which allowed it to collect biometric data on its users, including faceprints and voiceprints. Rather than explicitly informing its users about this change, the app vaguely communicated that they were issuing a “privacy update.” Once people found out what the update entailed, concern rightfully grew. This type of data collection indicates a significant shift from companies collecting behavioral data on their consumers to something much more invasive and without true consent. Only 36% of Americans trust tech companies using facial recognition technology. In general, public trust in Big Tech has been steadily falling in the United States. Regardless, however, most people still click “accept” to the Terms & Conditions on any website without actually knowing what is being agreed to, indicating a disconnect between what US citizens expect from businesses and what is actually being conducted. With a lack of national protection, nonprofit organizations must assume responsibility in protecting personal consumer data and using it ethically.
In the News: June 2022
How Technology Facilitates Culture Heritage Restoration and Preservation
This article presented projects and examples that have exemplified great progress in cultural heritage preservation. As these technologies continue to develop and experts in the field become more knowledgable and adept at using these technologies, there is a positive prospect that continually enhancing technologies will deliver further achievement in cultural heritage preservation and digitalization by human inventions and under human supervision.
What the Arts Need to Know about Big Tech
Upon broaching the subject of Big Tech, the consideration of arts organizations is often forgotten, and the focus is solely placed on Silicon Valley and the lucrative world within. But with the increased attention into the world of Big Tech (specifically Apple, Amazon, Alphabet [Google], and Meta [Facebook]) as a result of continual antitrust lawsuits, privacy violations, and the global struggle in creating effective policies to limit these companies’ powers, it is becoming more evident that the activities of Big Tech span across a variety of industries, the arts and nonprofit sector included. This article will provide an overview of the Big Tech monopoly over data and privacy through its cross-market domination and explain its effects on the nonprofit world.
Global Pandemic, National Response: A Survey of the Arts, Public Policy, and Technological Adaptation in Ireland
Something can be gained from examining the response of other nations and their arts and cultural sectors to the pandemic. Through this examination, lessons might be learned about how to continue the response in a time of unprecedented change. Within the past year and a half, many of Ireland’s arts organizations have found ways to create works that integrate emerging technology and also explore Irish identity. This research looks at some of those innovations and the public policies that supported them.
Arts Vibrancy and Digital Access: Part 2
Part one of this research looked at the relationship between broadband deployment and arts vibrancy in the United States, focusing on Texas. This article examines factors that are driving the digital divide and relatively low arts vibrancy in two counties on the Texas-Mexico border and how that could inform policies in the United States as a whole.
Comparing Digital Access with Arts Vibrancy in the U.S.
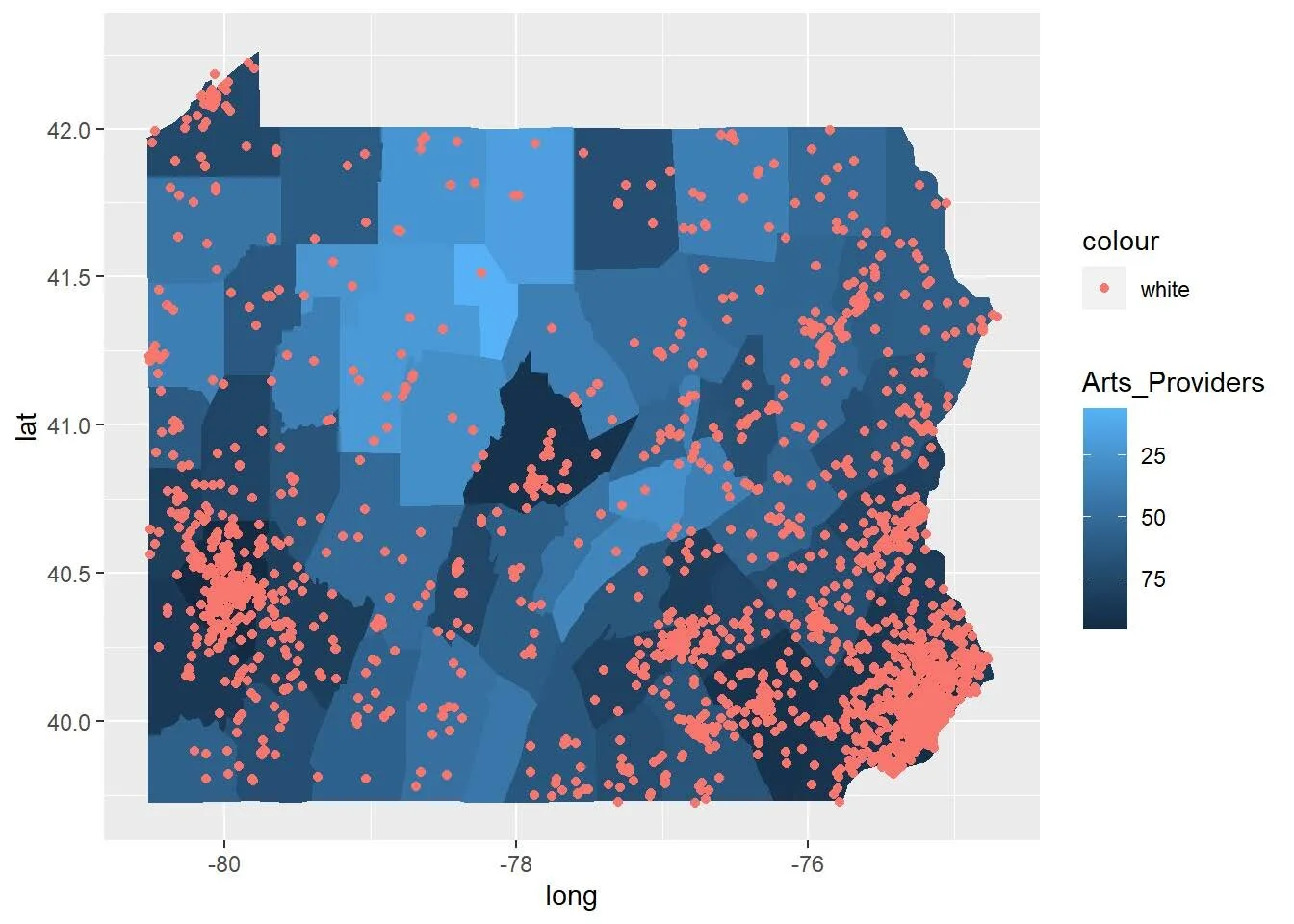
An estimated 18 million households in the United States do not have access to home broadband. This is a statistic that arts managers should consider when planning online programming and in-person events as the world opens up. By looking closer at the digital divide and comparing counties’ internet access to their arts vibrancy, as measured by SMU DataArts, this article will look at the United States’ digital divide and how it impacts opportunities for arts participation.
Part 2: Digital Access and Arts Vibrancy
Access to the arts is not even across the United States. The ways that people living in rural areas access artistic content differs from how people participate in urban centers. Additionally, as the sector is beginning to grapple with, access to the arts varies across racial and ethnic groups. Comparing county-level arts vibrancy data is one way to detect these patterns. While the number of dollars put into the arts in the form of compensation and expenses seems to be the best predictor of overall arts vibrancy, implementing municipal WiFi appears to be an opportunity for growth since analysis indicates that it can increase arts vibrancy.
Digital Inequity in the Arts: Part 1
The coronavirus pandemic has changed everything we assumed about the world. Everything that once seemed impossible to ask for in terms of public policy is now possible, including rent suspension, eviction moratoriums, and universal basic income. But, it has also revealed inequities, including who has access to the arts. This project, published in two parts, evaluates racial equity through the lens of the arts sector during the Covid-19 pandemic by asking the questions: who has access to the arts and, fundamentally, what does access look like?
Digital Privacy and Subversive Art
Having a better understanding of domestic legislation regarding digital privacy, as well as the international landscape as it pertains to these issues, can help in managing art that could be characterized as “seditious” or “radical.” It is important to note that surveillance, from both private and governmental entities, is on the rise as are the possibilities of censorship or unconstitutional oversight.