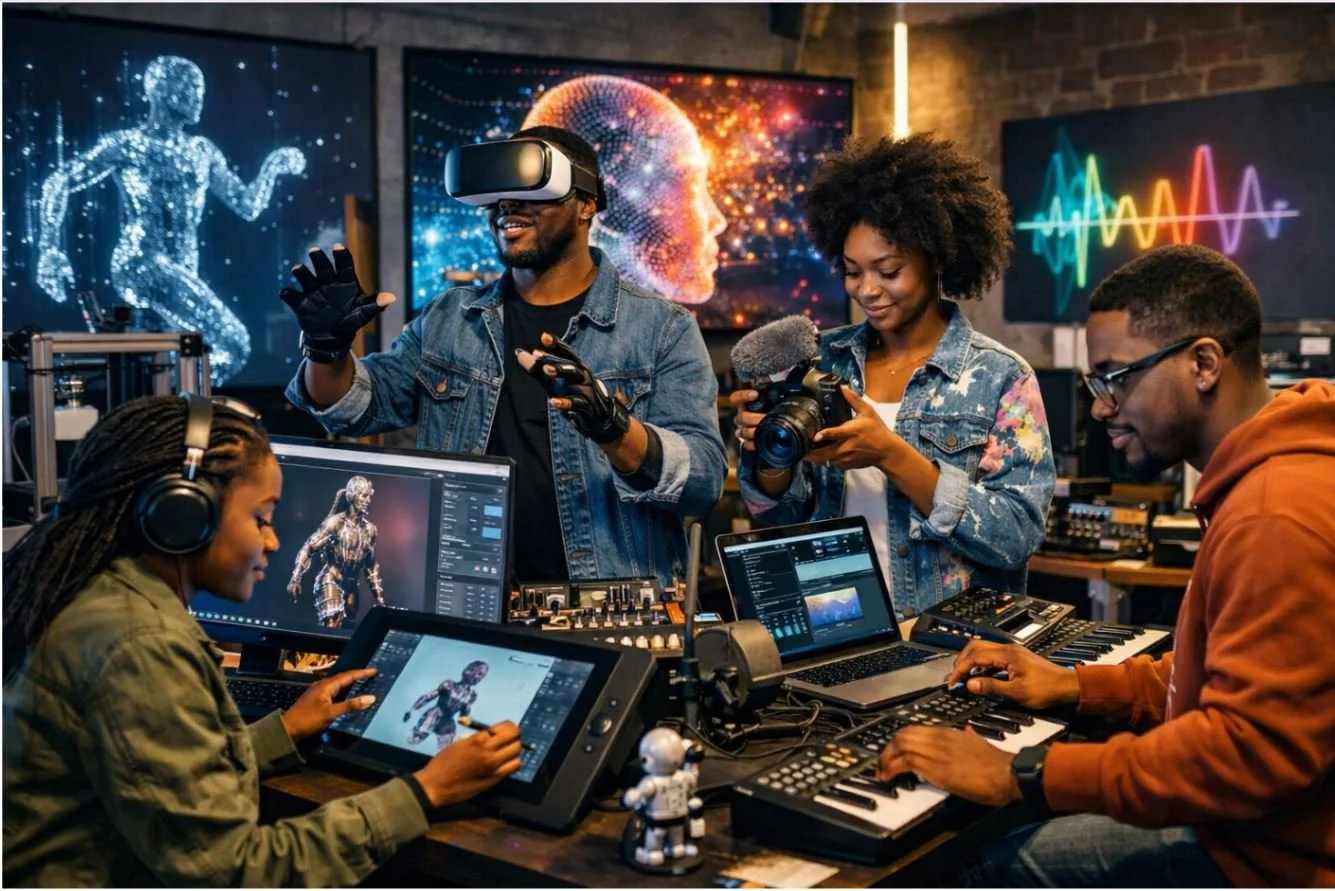
Google has been working on arts and culture platforms for several years now. AMT Lab has been reporting on it from the beginning. This #TBT explores the early days of the Google Arts & Culture Project and how it progressed into the app explosion earlier this year where Google used the selfie function on your phone to find artwork that looks like you.
#TBT: Gaga for Google
Today the news is buzzing with Google as they launch their Sidewalk Labs initiative in an effort to improve urban life. But here at AMT Lab, we have spent years dedicating posts to the many ways that Google products and services can improve arts management practices. This installment of Throwback Thursday will share several of them, drawing on posts that span as far back as 2008.
Bringing Art and Discussion to a Computer Near You: Introducing Google Art Talks on Google+
I am mildly obsessed with Google Cultural Institute. Why, you ask? It's two-fold. Firstly, Google has implemented its newest project to supplement the Google Art Project, Google Art Talks on Google+. As published on Google's Official Blog, "Each month, curators, museum directors, historians and educators from some of the world’s most renowned cultural institutions will reveal the hidden stories behind particular works, examine the curation process and provide insights into particular masterpieces or artists."
The Google Art Project and Art.sy: Exploration Engines for Art
The complexity and depth of the world’s art and culture is incredible and incredibly incomprehensible. Incredible because it evades definition and is relentlessly dynamic. Incomprehensible because the individual knowledge, time, and resources required to explore this cultural infinity are all too finite. Thus in this ever expanding universe, it is all too easy to gravitate towards the black hole of ignorance. But fear not, recent developments in technology are here to help steer us away from that ill-fated course. The upgrade of the Google Art Project and the launch of Art.sy are helping us understand our cultural universe, one art work at a time. With Google’s integrated documentation of the world’s museums, our artistic past is both nearer and clearer (literally, with a 7 billion pixel Rembrandt!). And Art.sy’s role as a “dynamic inventory” of emerging artists is an opportunity to discover contemporary art without being at the center of the artistic universe (New York or London).
The second phase of the Google Art Project has seen a massive expansion in the number of museums available on view. “Since last year, the Art Project has expanded its reach: 151 museums are now partners (compared to 17 in V1) providing over 30,000 artworks, from 40 countries (compared to 9 countries last year).”
From the National Gallery of Modern Art in New Delhi to the Getty Museum in Los Angeles, a visitor can experience a significant portion of the world as seen through objects, artifacts, paintings, and sculptures. Its new features include the ability to create your own collections and place them in personal “galleries”. The site also includes an entire section on ways to educate and be educated! For the initiated visitor, it is an invaluable opportunity for art historical exploration!
In its broader implications, the Art Project is a window into national identities as created through heritage and can be viewed as a vehicle for cultural diplomacy. This notion may seem overly ambitious, given the sites’ hyper-virtual immersion in a country’s artistic wealth and apparent disregard of chronology. But it exists nonetheless, as a weaker current that may invoke some to pursue additional research, and even create travel plans!
Additionally, the countries represented benefit from showcasing the wealth of their museum’s collections on an integrated domain, alongside world-renowned museums such as the Met. In essence, the Google Art Project acts as a virtual art fair for the world’s museums. It can either be surveyed at a harried pace or explored with deliberation. Either way, you get to collect works and create galleries for no cost at all!
In a similar vein to the Google Art Project, Art.sy is helping the world discover contemporary art, a category that often transcends national boundaries and is increasingly difficult to keep up with, let alone understand! With Art.sy the difficulties of “discovering fine art” are eased with the development of the Art Genome Project, “an ongoing study of the characteristics that distinguish and connect works of art.”
The website recently launched its beta version and some of its remarkable features were highlighted by the lucky few who were given access. Essentially, Art.sy allows users to discover new artists and works based on a set of 800 characteristics or genes that are assigned to each work of art. Given a user’s interest in a work of art and the underlying genes that are encompassed within, it suggests additional work that may interest them. Users can also choose to follow an artist or a gallery and of course, contact the gallery if they are interested in making a purchase.
A review by BetaBeat praised the site for its ability to lead an average art appreciator “to artists like Sherin Guirguis, a young Egyptian artist whose abstract paintings resemble fractals and eyeballs.” At the same time, it was criticized for only having secured partnerships with the leading galleries of the world and effectively limiting the art on view. Art.sy also retains an air of exclusivity, one that it may carry with it into the future.
Nevertheless, it would be remiss not to give the unique and brilliant workings of Art.sy a try.
In effect, both Art.sy and the Google Art Project are innovative discovery engines for art. The differentiation lies in that the former knows where you are headed even as you might not. The latter, in contrast, lets you meander your way to a destination unknown, an artwork unseen.
The Google Art Project Welcomes You to the White House
 Ever wanted to take a tour of the White House? Well now you have a chance, and you can do it all from the comfort of your living room.
The Google Art Project, a site devoted to presenting high resolution photographs of hundreds of works of art and museum tours from some of the finest museums in the world, including the Palace of Versailles, the Van Gogh Museum and the Metropolitan Museum of Art, has unveiled its latest project, a captivating look inside the world’s most famous residence, the White House.
Ever wanted to take a tour of the White House? Well now you have a chance, and you can do it all from the comfort of your living room.
The Google Art Project, a site devoted to presenting high resolution photographs of hundreds of works of art and museum tours from some of the finest museums in the world, including the Palace of Versailles, the Van Gogh Museum and the Metropolitan Museum of Art, has unveiled its latest project, a captivating look inside the world’s most famous residence, the White House.
As part of what the White House calls its “commitment to opening the doors of the White House to all Americans,” the site primarily does two things. First, it presents images of dozens of paintings and works in art in stunning high resolution quality; and secondly, my favorite part, it offers a 360-degree view of many of the “public” areas of the White House, giving you your own personal tour!
The White House is the latest location added to Google’s Art Project website, which has steadily grown in recent months by adding some of the top museums in the world to its collection. It really is a site to behold and a must visit for arts lovers everywhere; by taking some of the world’s best collections and putting them online free of charge for the world to see, it really does represent one of the best ways to merge technology with the arts to generate enthusiasm and excitement for the stunning works of art that are now viewable in all their high definition glory.
For the paintings and works of art themselves, Google features what they call a “gigapixel” camera that offers an extremely high resolution look at some of the most famous paintings in the White House collection, including Gilbert Stuart’s famous portrait of George Washington. Viewers can zoom in and examine the paintings in EXTREMELY close detail, all the way down to the brushstrokes, just as you would if you were to view them in person, right?
You’ll find hundreds of paintings, sculptures, pieces of furniture, and more available for view. You’ll also find a portrait of almost every former president as well. Some of my favorite presidential portraits, which I have seen before on either book covers, in print or elsewhere, were immediately noticeable and fascinating to view up close and in so much detail. Some of my favorites include Aaron Shikler’s portrait of John F. Kennedy, John Singer Sargent’s portrait of Teddy Roosevelt, George P.A. Healy’s portrait of a sitting Abraham Lincoln, and last by not least, John Trumbull's portrait of my favorite founding father, Alexander Hamilton.
The coolest part of the site however, if you’re like me, is the virtual tour. In recent months, Google has made headlines by starting to take their Street View cameras indoors to start photographing businesses and places of interest to add to its Google Maps site. What Google has done here is to take those Street View cameras inside the White House and presented a “museum view” of the public spaces inside. Here is where you can walk around and give yourself a tour of two floors of the White House, seeing sights like the East Room (where indoor press conferences are usually held) and the China Room, where presidential china collections dating back to the 18th century are held.
Not everyone will have the chance to visit Washington and take the White House tour (which is a hard ticket to come by, and even if you can get on the list, usually requires a several months long wait), but thanks to Google, we now have the next best thing, viewing many of the sights you would see on a tour on your computer screen.
This may be one of the few things everyone can agree on when it comes to the White House: having an opportunity to view the magnificent works of art from the White House collection in such high resolution is a welcome treat, and worthy of praise. I encourage everyone to check out the site and go exploring!
The Year That Was
The clock’s ticking is becoming ever more pronounced, 2011 shall soon be placed in the archives of our collective history. So as we bid farewell to this year, let’s not forget the events that made the technology-art axis rotate for a full 365 days!
The year began with the unfolding of the Google Art Project, which revolutionized not only the way we view and how much we could view of an artwork, but also how art in museums became accessible at a global level.
And as art became accessible to a host of people, people became accessible to arts organizations through crowdsourcing. This year, we saw an incredible rise in the use of crowdsourcing, in many different areas and for many different purposes. Operas were crowdsourced, exhibitions were crowdsourced, and even art-works were crowdsourced. But it was the concept of crowdfunding that received a standing ovation from a crowd of people, organizations, and artists.
And in the pockets of these crowds of people were smart-phones and tablets, all glowing with the slide-to-unlock signs. With the rise of the iPhone/Droid/Blackberry and the iPad, many museums developed apps for specific artists or exhibitions in order to augment and guide the viewing experience. In fact, apps revolutionized the way audiences interact with art and museums were quick to capitalize on this opportunity.
Moreover, some galleries and museums relocated to the online world, and entire exhibitions moved from the realm of the physical to that of the virtual. Paddle8 and Art Micro-Patronage were both introduced this year, and only time will tell whether online exhibition spaces can be just as successful as offline ones. Moreover, there was an increasing emphasis on tailoring the arts towards one’s aesthetic and visual interests through Art.sy and Artfinder, the Pandoras of the art world. Additionally, s[edition] rebelled against the procurement of tangible art forms through its effort to sell digital limited edition prints of big name artists such as Damien Hirst and Tracey Emin.
As always, social media analytics remained at the forefront, and arts organizations realized the importance of sharing and conversing with their audiences through social media platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, and Google+. Many studies were done on Millenials and their motivations, which helped organizations engage and connect with this tech-savvy generation.
And as conversations became heated in social platforms, the world of art and technology did not let us forget that Earth itself is experiencing global warming. There were some excellent fusions of art and technology aimed at the problem of climate change and the move towards green energy by organizations such as GlacierWorks and SolarFlora.
But what will the year 2012 bring in the technology-arts realm? Innovation, progress, the unexpected, awe , wonder, but surely not an apocalypse, right?
Happy New Year!
Leveraging the Virtual and the Real
The art world is experiencing a virtual boom. A boom that began with the advent of the street view technology used by Google, which has now forayed into the world of art. Within the last two years, the Google Art Project has photographed, digitized, scaled, and organized some of the most famous artworks in renowned galleries and museums such as the Tate, the Uffizi Gallery, and the Palace of Versailles. Moreover, this digitization of famous artworks is not any mere reproduction; rather it is a reproduction of the grandest or perhaps the smallest of scales: gigapixel images.
Photograph by Amantini Stefano/4Corners Images
This technology has revolutionized the way we interact with art even though it can in no way be deemed an equal alternative to the real experience. The digitization of museums and galleries has captured their tangible and physical aspects, but not their essence. A visit to the Palace of Versailles will never compare to visiting a website. So the question begs to be asked whether this virtual experience guides, develops, and enhances our real experience. Does the virtual help the real? And what can arts organizations gain from this insight?
Detail from Sandro Botticelli’s Birth of Venus (from the Uffizi Gallery, Florence)
A visitor recently set off an alarm, a really loud alarm, in a museum in Basel when she got too close to an artwork. This encounter illustrates how a public viewing experience within the confines of a gallery or a museum can act as a barrier. More often than not, we are afraid to get too close to painting, even though we want to (with the exception of the aforementioned visitor, of course). We also feel the need to constantly move from one painting to the next until we reach a point of complete and utter visual saturation, perhaps even visual exhaustion.
In the virtual confines of the Google Art Project, we can get eerily yet brilliantly close to our favorite artworks on our very own laptops. We can see details that could not have been physically possible under any circumstances in a museum setting. We can also pause for as long we please and we can leave and return as we please. On a whole, a virtual art world as powerful as that of the Google Art Project enriches and builds upon our real experiences.
Detail from Louise Elisabeth Vigée-Lebrun’s Marie-Antoinette de Lorraine-Habsbourg, Queen of France, and her children (from the Palace of Versailles)
Yet, however exquisite and detailed the world of the Google Art Project may be, unlike the masterpieces it virtually showcases, it cannot boast of having attained perfection. An article in the Daily Beast highlights the fact that while the Google Art Project has enabled us to view artworks in a manner that is unprecedented, it is not clear whether we are seeing better.
In the same vein of thought, the author of a blog post in Freize argues that by bringing us closer to works of a bygone era, such as Caspar David Friedrich’s The Monk by the Sea, the Google Art Project has ignored the dynamism of the art world, where the concept of a masterpiece and the artist genius are constantly evolving. The post also mentions how Google is guilty of not explaining to us why certain artworks were, and still continue to be, worthy of the title of a masterpiece.
The Monk by the Sea, Caspar David Friedrich (from the Alte Nationalgalerie, Berlin)
For arts organizations looking to create a virtual experience, let’s analyze the advantages and the disadvantages. A virtual experience can create a longing and desire for a real, physical experience. The aforementioned article in the Daily Beast provides an interesting insight from the Director of MoMA about virtual outreach: the virtual presence and proliferation of art works housed at the MoMA actually compelled the true lovers of art to seek out the real. Consequently, the MoMA has had a twofold increase in attendance over the last ten years.
Another big advantage is increased accessibility to audiences around the world. But accessibility alone is not adequate and arts organizations should be wary of becoming just another collection of images on the World Wide Web. The aim is to educate people and generate interest, not pander to their aesthetic appetites. A virtual experience that is no different from a collection of images limits the potential of technology as a vehicle for education, discussion, thought, and reflection. Thus, arts organizations should look further than the potential of the online world as a visual cache because only then will they truly be able to leverage the virtual and the real.