Streaming technology in the last decade has rebuilt the structure of film revenue models. Motion pictures now earn revenue through a network of internet-based over-the-top (OTT) content distributors, reaching worldwide audiences by partnering with multiple streaming platforms. More recently, the Covid-era decline in theatrical film distribution has led to a purely OTT distribution model, and a complete reliance on internet-based revenue. Independent production companies often skip theatrical releases entirely and go straight to market through OTT streaming platforms, which range from smaller niche entities to major corporate juggernauts. Internet-based technological advancement has allowed for this change to occur; new technologies induce new revenue. In the future, advancements in blockchain technology are expected to disrupt and further redesign the film distribution waterfall.
The Distribution Waterfall
In film and television, the market flow of revenue is referred to as the "distribution waterfall." As audiences engage with a new film, revenue is generated at each point of contact. Distributors collect this revenue, take a small cut for themselves, and pass along the money to the film's producers. Revenue works its way down the value chain, and the film's initial investors are recouped with interest. If a movie is profitable, then earnings are divvied up in the form of royalties, according to a previously agreed upon distribution plan. This plan is specified according to a film's CAMA (Collective Arts Management Agreement), a third-party account which collects film revenue and distributes royalty payments. Royalty payments are the final step in a distribution waterfall.
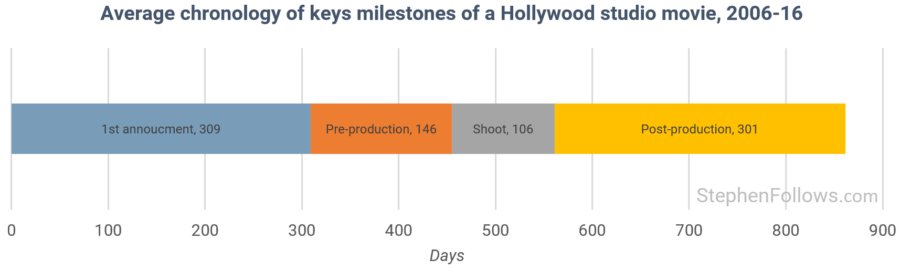
There are a few financial aspects to note about the independent film industry, the most serious being the necessary front-loading of a project's cash flow. As opposed to major studios, who can produce an upwards of 20 films a year and operate on multi-billion dollar budgets, the independent film industry is characterized by studios who produce one film a year, with mid-range budgets of $2-10 million. Regardless of budget size, feature films take a long time to create, as show below in Figure 1. Once pre-production begins, revenue streams may not materialize for years. That is why film producers need investors - it takes a sizable amount of working capital to build and operate a production machine.
Figure 1: From 2006 to 2016, average Hollywood movie productions were announced 871 days before theatrical release. Source: StephenFollows.
An additional note – the majority of independent films do not turn a profit. Monetization is unpredictable, volatile, and varies across film genres. For a given independent film, the majority of film investors do not see a full return on a given investment, exemplified by Figure 2. Though box office revenues from the past 20 years are more easily accessible, the revenue generated from OTT streaming platforms is usually kept secret by distributors, sales agents, and producers. Given the scope of this report, today's OTT ROI averages are inaccessible, but will likely be similar to the averages seen in the past two decades or so.
Figure 2: From 1999 to 2018, average domestic indie movie profitability wavered between 12-42% depending on genre. Source: StephenFollows.
Emerging Revenue Opportunities
Today, there is a new digital revenue source in popular media – the Non-Fungible Token, or NFT. Conceptually, NFTs are conventional; not all NFTs are digital. Modern society relies on non-fungible tokens to prove identity. A driver's license is a non-fungible, inimitable token which establishes proof of driver qualifications. A birth certificate is a non-fungible token which certifies the date and time of one's birth. These tokens cannot be copied or altered – they are one of a kind.
The main difference between conventional NFTs and digital NFTs is the ability to buy and sell digital NFTs. Commercial NFTs are digital assets - marketable investments that may accrue value over time. Digital NFTs are built on blockchain technology and sold using cryptocurrency, meaning every peer-to-peer transaction is recorded on a decentralized public ledger.
The decentralized nature of blockchain technology has led to serious global innovations in healthcare, immigration, shipping, and real estate. In the art and entertainment sector, NFTs are quickly proving their own worth, being sold as collectors items, artistic merchandise, and within the film industry, vehicles through which investors pay to access exclusive content and potentially earn royalty points. The aim of this article is to demonstrate how these emerging sources of revenue are impacting the modern distribution model in independent film.
Why Filmmakers Should Care
Short answer: More revenue for your team.
Below is a film distribution waterfall for a film production that has incorporated elements of Blockchain technology. Note the flexible nature of NFT revenue – these tokens can be sold at any stage in the production process. NFTs are often used in merchandising, which seems to be their most popular application to date. However, certain production companies are now incorporating royalty options into their NFTs to attract stakeholders. Essentially, any NFT enthusiast could become an accredited investor in a major motion picture.
Figure 3: Revenue distribution waterfall for an independent film utilizing NFTs. Created by author.
Smart Contracts Explained
This brings up an important aspect of NFT functionality – smart contracts. During the NFT creation process, programs may be installed that run when predetermined conditions are met. These programs are phrased as a collection of "if/then" statements. For instance, one may create an NFT smart contract stating: "If this NFT is purchased before 2022, then the purchasing party will receive 3 royalty points from the investor pool of Spielberg's next movie." Once Spielberg's next movie hits the market, and the first hurdle (presented in step 5 of the infographic above) is passed, that NFT owner will automatically begin to earn 3% from the investor pool. This royalty payment is automatic because smart contracts are automatic – they are written into cryptocurrency and activated each time a new transaction occurs. Therefore royalties in the form of cryptocurrency would automatically flow into the NFT owner's virtual wallet.
Smart contracts may also be written as "when/then" statements. These can be used to program royalties within NFT's: "When this NFT is resold to another party, Spielberg will receive 10% of the revenue from the resell transaction." In this way, Spielberg could earn 10% royalties for every future purchase of his NFT, meaning hypothetically endless royalty payments. For merchandising, this means serious opportunities for long-term revenue generation. If someone creates and sells an NFT featuring a little-known actor, and then that actor becomes an international sensation, the NFT may then fetch serious dividends for the creator.
Smart Contracts Drive the Waterfall
As blockchain technology and cryptocurrency becomes more integrated into the film production model, the integration of smart contracts will completely automate steps 4-7 of the waterfall model in the above infographic. No longer will the distribution waterfall require third-party rights management and royalties collection agencies. New CAMAs will be crypto-based digital wallets, and revenue streams will be distributed automatically through smart contracts once transaction thresholds are met. Smart contracts may be designed based on stipulations written within a movie's PPM agreement, though it is important to note that PPMs are not contracts, but disclosure documents meant to contain investment information in plain language. Still, PPMs contain the fundamental guidelines needed to ensure the CAMA’s distribution waterfall flows correctly.
Through the adoption of decentralized investment platforms, the integration of PPM-based smart contracts, and the minting and selling of NFTs, the indie film distribution waterfall is evolving in ways that maximize potential revenue, improve latency, and eliminate obsolete intermediaries. Crypto film production is still in its infancy, but the booming NFT market is sure to integrate itself further into the indie production machine. New doors are opening up for content creators. Ambitious filmmakers should have a clear understanding of how revenue distribution waterfalls work before they tackle a blockchain-based film production.
+ References
Alava, Patricia Corral. "How to monetize video - AVOD, SVOD, TVOD & PVOD Explained." Kaltura Media Channel. Published July 1 2021. https://corp.kaltura.com/blog/avod-svod-tvod-explained/
Beenen, Wieke. "Blockfilm Becomes Leading Blockchain-Based Film Financing Platform after Groundbreaking OSC Exemption Order." The Blockchain, June 25, 2021. https://www.the-blockchain.com/2021/06/24/blockfilm-becomes-leading-blockchain-based-film-financing-platform-after-groundbreaking-osc-exemption-order/.
Bernstein, Paula. "How to Determine the Right Budget Level for Your Film." IndieWire, October 28, 2015. https://www.indiewire.com/2015/10/how-to-determine-the-right-budget-level-for-your-film-56083/
Castor, Amy (moderator). "The Impact of Blockchains for Emerging Economies." Ethereal Virtual Summit 2020, Ethereal Summit. Published May 2020. Accessed September 2021. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=khvuq-zjPjg
Chandler, Simon. "This Is How NFTs Might Change TV and Film Industries." Crypto News, October 3, 2021. https://cryptonews.com/exclusives/this-is-how-nfts-might-change-tv-and-film-industries.htm.
Cervantes, Edgar. "28 movies released early via streaming." Android Authority, July 12, 2021. https://www.androidauthority.com/movies-released-early-streaming-coronavirus-1096141/
Cohen, Evan. "What are NFTs & Why Are Top Collectors Going Digital?" Learn with Vincent, July 1, 2021. https://www.withvincent.com/learn/what-are-nfts
Daley, Sam. "How Using Blockchain in Healthcare is Reviving the Industry's Capabilities." Builtin. August 6, 2021. https://builtin.com/blockchain/blockchain-healthcare-applications-companies
Dreier, Troy. "How Vimeo Pivoted Away from Original Content and Found Its Niche." Streaming Media Magazine, 31 Jan. 2019. https://www.streamingmedia.com/Articles/Editorial/Featured-Articles/How-Vimeo-Pivoted-Away-From-Original-Content-and-Found-its-Niche-129733.aspx?utm_source=related_articles&utm_medium=gutenberg&utm_campaign=editors_selection.
Durta, Andre; Tumasjan, Andranik; Welpe, Isabelle M. "Blockchain is Changing How Media and Entertainment Companies Compete." Sloan Management Review, Massachusetts Institute of Technology [MIT]. Fall 2018.
Erbland, Kate. "Highest grossing indie films of 2021: 'Copshop' Breaks Through in Action-Crazy Specialty Box Office Rankings." IndieWire, September 28, 2021. https://www.indiewire.com/feature/highest-grossing-indie-films-2021-1234607448/
Fanea-Ivanovici, Mina; Hasnan Baber. "Crowdfunding model for financing movies and web series." International Journal of Innovation Studies, Volume 5, Issue 2, Pages 99-105, June 2021. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2096248721000126
Ferrari, Alex; Jackson, Kim; Cloven, Jake. "Indie Film Hustle - Using Blockchain to Make Money with your film." Indie Film Hustle Podcast. Published August 3, 2021. Accessed October 16, 2021. https://indiefilmhustle.com/kim-jackson-jake-craven/
"Film & Video - Quarterly Update." Fort Mill, South Carolina: Mergent, September 20, 2021. https://www-proquest-com.cmu.idm.oclc.org/reports/film-amp-video-quarterly-update-9-20-2021/docview/2576905073/se-2?accountid=9902
"Film Private Placement Memorandum: What is a PPM? How Does it Fund Your Film?" FilmProposals. Accessed October 15th, 2021. https://www.filmproposals.com/film-private-placement-memorandum.html
"First Feature Film NFT Drops from Vuele™ Grossing Nearly Six Figures in Four-Day Auction with Academy Award®-Winner Anthony Hopkins Thriller Zero Contact." Yahoo! Finance, Yahoo!. September 29, 2021. https://finance.yahoo.com/news/first-feature-film-nft-drops-143000055.html.
Follows, Stephen. "What percentage of independent films are profitable?" StephenFollows, Film Data and Education, October 7, 2019. https://stephenfollows.com/what-percentage-of-independent-films-are-profitable/
Follows, Stephen. "How long does the average Hollywood movie take to make?" StephenFollows, Film Data and Education, May 7, 2018. https://stephenfollows.com/how-long-the-average-hollywood-movie-take-to-make/
Gomez, Alex W. "NFT Royalties: What Are They and How Do They Work?" Cyber Scrilla. Accessed October 13, 2021. https://cyberscrilla.com/nft-royalties-what-are-they-and-how-do-they-work/
Hrbek, Deborah. "Independent Film Financing - How It Works." Hrbek Law. Published April 2008. Accessed October 16, 2021. https://www.hrbeklaw.com/independent-film-financing-how-it-works.html
Hurtado, Patricia. "Steven Seagal on Hook for SEC Crypto Fine Despite Move to Moscow." Bloomberg Markets. Bloomberg, August 27, 2021. https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2021-08-27/steven-seagal-on-hook-to-sec-over-crypto-fine-even-in-moscow.
Investopedia Team. "How Blockchain Is Revolutionizing Content Distribution." Investopedia. Dotdash, June 9, 2021. https://www.investopedia.com/news/how-blockchain-revolutionizing-content-distribution/
Iyer, Jenee. "NFTs Legal Considerations And Implications." Arts Management and Technology Laboratory, September 12, 2021. https://amt-lab.org/blog/2021/9/nft-considerations-and-implications
Kiderlin, Sophie. "NFT sales volume soared to $2.5 billion in the first half of 2021, as artists, celebrities and even Twitter and CNN joined the crypto craze." Market Insider, Jul 7, 2021. https://markets.businessinsider.com/news/currencies/nft-value-sales-h1-dappradar-nonfungible-tokens-crypto-hype-2021-7
Kroll, Noam. "Why NFTs Will Become The Great Next Revenue Stream For Filmmakers." Noam Kroll, March 4, 2021. https://noamkroll.com/why-nfts-will-become-the-great-next-revenue-stream-for-filmmakers/
Letson, Omar. "A Record Breaker: Netflix Signs Its Most Expensive Deal Ever for $700 Million." TheRichest, October 2, 2021. https://www.therichest.com/rich-powerful/a-record-breaker-netflix-signs-its-most-expensive-deal-ever-for-700-million/.
Liebkind, Joe. "How Blockchain Technology is Changing Real Estate." Investopedia, March 22, 2020. https://www.investopedia.com/news/how-blockchain-technology-changing-real-estate/
Lindlahr, Sebastian. "Digital Media Report 2021 - Video-on-Demand." Statista Digital Market Outlook. Published August 2021. Accessed September 2021. https://www-statista-com.cmu.idm.oclc.org/study/38346/video-on-demand/
Low, Elaine. "Netflix reveals $17 Billion in Content Spending in Fiscal 2021." Variety, April 20, 2021. https://variety.com/2021/tv/news/netflix-2021-content-spend-17-billion-1234955953/
Mink, Casey, and Cindy Cowan. "Is Mogul Productions the Bitcoin of Film Financing?" Backstage, April 15, 2021. https://www.backstage.com/magazine/article/mogul-productions-cindy-cowan-73061/.
"Motion Picture Production & Distribution - Quarterly Update." Fort Mill, South Carolina: Mergent, September 6, 2021. https://www-proquest-com.cmu.idm.oclc.org/reports/motion-picture-production-amp-distribution/docview/2576904636/se-2?accountid=9902.
News by Florian. "Blockchain technology for managing migration into the EU." MiiCT (ICT Enabled Services for Migration), Sept 7, 2019. https://www.miict.eu/2020/09/07/blockchain-technology-for-managing-migration-into-the-eu/
Nossa, Daniel. "PPM Standardization in Security Token Offerings." Steptoe & Johnson PLLC. Published Feb 2019. Accessed October 2021. https://www.steptoe-johnson.com/sites/default/files/PPM%20Standardization%20in%20Security%20Token%20Offerings.pdf
Palaiokrassas, Georgios, et al., "Deploying Blockchains for a New Paradigm of Media Experience." International Conference on the Economics of Grids, Clouds, Systems, and Services (GECON), pp 234-242. Published Feb 2019. Accessed September 2021. http://bloomen.io/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/ICCS-gecon-Palaiokrassas-Deploying-blockchains-for.pdf
Pope, Stephen. "Blockchain to be a Gamechanger for Global Shipping." Forbes, Oct 16, 2019. https://www.forbes.com/sites/stephenpope/2019/10/16/blockchain-to-be-a-gamechanger-for-global-shipping/?sh=709ebc7b512a
Poullain, Anna (moderator). "Emerging Economies Improving With Blockchain?!" AIBC Summit Malta, American Independent Business Coalition. Malta Fairs and Conventions Centre. Published Feb 12, 2020. Accessed September 2020. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=forpAAQeEXE
Princess. "Mondo Launches NFT Series For Film Franchise Collectibles on VeVe App." NFT Evening, July 21, 2021. https://nftevening.com/mondo-launches-nft-series-for-film-franchise-collectibles-on-veve-app/
"Ryan Kavanaughs Media Firm Secures $100 Million Investment for Crypto Project." Financial Services Monitor Worldwide, May 24, 2019. https://www-proquest-com.cmu.idm.oclc.org/wire-feeds/ryan-kavanaughs-media-firm-secures-100-million/docview/2229616124/se-2?accountid=9902.
S. He, Q. Tang, C. Q. Wu and X. Shen, "Decentralizing IoT Management Systems Using Blockchain for Censorship Resistance," in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 715-727, Jan. 2020, doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2939797.
Sreenivasan, Harry. "Can blockchain help fill journalism’s funding gaps?" PBS NewsHour. Published September 2018. Accessed September 2021. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dXwfUNXKv3E
Schonberger, Jennifer. "Hollywood Taps into NFT Craze with Anthony Hopkins Movie, Using Blockchain for Auction." Yahoo! Finance. Yahoo!, September 28, 2021. https://finance.yahoo.com/news/hollywood-taps-into-nft-craze-as-anthony-hopkins-movie-uses-blockchain-for-distro-183733236.html.
Shepherd, Adam. "Blockchain Adoption in Broadcast." IBC. International Bancshares Corporation, August 8, 2019. https://www.ibc.org/trends/blockchain-adoption-in-broadcast/4253.article.
Tham, Su Fang. "The Fi Hall of Fame: Mo' Money, No Problems - A Producer's Guide to Residuals." Film Independent, September 24, 2021. https://www.filmindependent.org/blog/mo-money-no-problems-producers-guide-residuals/
"The Mobile Internet Phenomena Report." Sandvine. Published May 2021. Accessed September 2021. https://www.sandvine.com/hubfs/Sandvine_Redesign_2019/Downloads/2021/Phenomena/MIPR%20Q1%202021%2020210510.pdf
Velikovsky, JT. “Storyality #24 – on Feature Films and Roi (Return on Investment).” StoryAlity, April 28, 2012. https://storyality.wordpress.com/2012/12/17/storyality-24-on-feature-films-and-roi-return-on-investment/'.
Wescott, Kevin et. al., "Digital Media Trends, 15th Edition." Deloitte. Published April 2021. Accessed September 2021. https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/technology/digital-media-trends-consumption-habits-survey/summary.html
"2021 Global Networking Trends Report." Cisco. Published 4Q 2020. Accessed September 2021. https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en/us/solutions/enterprise-networks/2021-networking-report.pdf