In the visual arts, there is no guarantee that work will be preserved for any time after it has been created. While physical pieces are certainly more permanent that performances, all works are subject to deterioration and destruction. Some pieces are more susceptible, such as work made of fragile material or located in an unstable environment, but all pieces will eventually face wear and damage. Restoration is thus required in order to renew pieces to their original and/or best form. Ultimately, the goal of restoration is to safely and accurately bring pieces to their best form for study and public enjoyment. Through technology, this goal can be accomplished.
In the News: July 2022
July has been a whirlwind of a month at the intersection of art and technology. From possible successful legislation on data privacy in the US, to the Italian government putting its foot down on NFT sales, or just an AI making uncanny valley art that is starting to get a little too real, a lot has happened in the world. The spread of articles below give a glimpse into a small portion of the interesting events that have occurred this month!
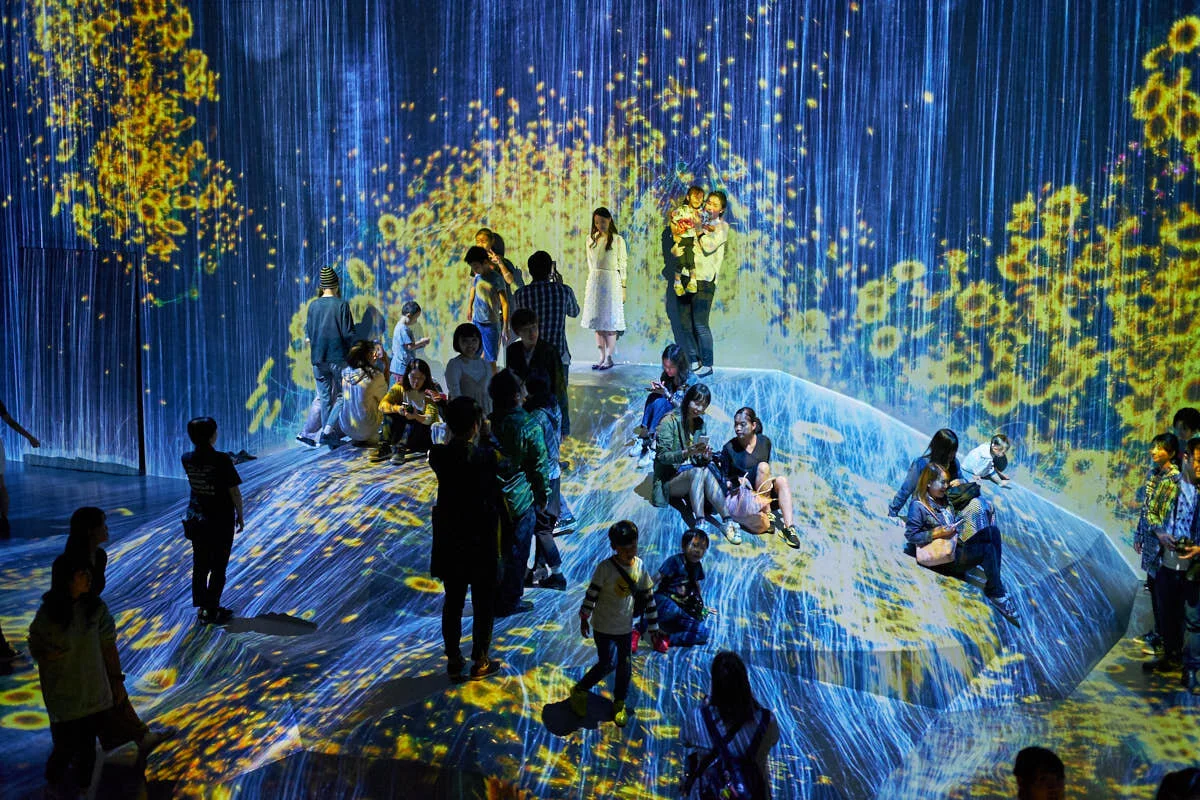
Artistic Futures: Digital Interactive Installations
The concept of interactivity in the artistic field became popular in the 1950s due to the realization that interactive art could serve as a bridge between connecting artists and audiences in new ways. More importantly, audiences were able to become part of the artwork through their expression in experiencing the artistic process. These advances have led to greater accessibility in individuals’ artistic experiences. Moreover, the physical return to museums and galleries post-covid enhances digital interactive installations since audiences can experience this art live in a physical space, fostering a new sense of curiosity and community. The more frequent implementation of digital interactive installations in the technological age is just the beginning of its artistic evolution. The digital world of art is a hub of creativity and eager exploration, paving the way for a bright and innovative future for a fairly new form of art.
Crypto Art's Origins and Future
Our recent articles have examined NFTs’ recent rise and issues surrounding their environmental impact. This article looks more in depth at crypto art’s origins and the place it will hold in the future. Crypto art will continue to advance and evolve, so understanding its current impact will help those in the art world maximize its potential.
NFTs: A New Age of Digital Art
In recent months, NFTs have had a large presence on news feeds, especially in artists’ circles. NFTs, or non-fungible tokens, are “digital assets that [represent] real-world objects like art, music, in-game items and videos.” Because of this, they are challenging the traditional ways that people view, buy, and sell artwork. This research will look at how NFTs came to be and what artists and arts administrators should consider when utilizing this technology.
AI-assisted and AI-powered Art: Different Challenges for Digital Preservation
Artists are among the many professions that are embracing artificial intelligence. AI is beginning to undertake tedious repetitive work, without replacing human’s creativity. Recently, the art market has displayed an interest in purchasing AI art. Christies sold Edmond de Belamy, an algorithm-generated painting, and Sotheby’s sold Memories of Passersby I, an AI video installation, at $432,500 and $51,012, respectively. With a rapidly increasing variety of AI art being created and transacted, the need to preserve such art in differentiated ways is emerging.
Livestreaming for Regional Theatre: History and Perspectives: Part 1
This is a two-part series exploring how the benefits of incorporating livestreaming technology into theatres. Part 1 of the report documents a history of livestreaming theatre (involving a timeline and the lifespan of the industry’s biggest players) and a brief analysis of what it means to perform “Live!” and its programming potential.
AI as a Tool in the Arts
Artists are taking advantage of new technologies to enhance their artmaking. They are using AI as a tool in the same way that artists of yesteryear used pen and ink and paintbrushes. This opens a whole new realm of possibilities for arts managers in terms of the scope of multimedia exhibitions and performances. Artists who are using AI as a tool include visual artists, performers, and creators of popular media.
Crowdsourced Digital Art Projects: Centralization and Agency
As digital crowdsourced art continues as a mode of art making, it is necessary to developed an understanding of which features of digital arts programming are crucial in the engagement of digital audiences. The following analysis of four digital art projects focuses on the participatory, rather than the interactive, specifically projects wherein audiences become artists by participating in the creation of a piece of art by making one or more creative contributions. Perhaps not surprising, agency and control were identified as significant to participation.
News Roundup: New Possibilities In 3D
AMT-Lab contributors are always looking at all sorts of new technologies in the world of 3D. With the increasing popularity of technologies such as 3D printing, the possibilities continue to emerge. These new technologies and their uses in the art world keep us interested in how the intersection of art and technology impact our world.