INTRODUCTION
Generative AI (GenAI) has become increasingly integrated into marketing and communication careers, and even our daily lives, with the rise of various text-to-image (Like DALL-E, Midjourney, or Craiyon), text-to-video (Sora), & text-to-text tools (ChatGPT or Claude). As digital marketers find new and innovative ways to keep up with the trends, particularly those reaching GenZ in a quick-changing popular culture scene, how are they reacting to the rise of GenAI?
Image: Human and Artificial Intelligence getting a drink together
Image Source: Worklife
GENERATIVE AI - PAINS AND GAINS
To be able to set the stage and fully understand the capabilities of GenAI in 2024 it is important to first look at the success stories and blunders of the tool. GenAI has proven to be useful in an organization’s practices, specifically for creating attention-grabbing headlines that please SEO (search engine optimization) results, creating unique instances of image synthesis in seconds that would otherwise take significant time to create, and just for general entertainment purposes that keep audiences engaged. However, as a society we’ve seen many mistakes occur in the practices of GenAI. There are many missteps an eager marketer can make:
Relying too heavily on the use of GenAI
Failing to verify the validity of the content that is generated
Lacking insight into legal issues (especially regarding the copyright issues surrounding artists and AI rights)
Using AI in already established relationships with audiences
Failing to train AI to use your organization’s tone and voice
Some organizations that relied too heavily on GenAI in 2023 dealt with the following issues: Sports Illustrated using AI-generated authors and articles, fake citations from ChatGPT used by an attorney, an automated poll appearing on an MSN article about a woman who was found dead, and Samsung employees pasting confidential source codes into ChatGPT… to name a few. Given this insight, the question posed for marketers today is surrounding the value of GenAI in their marketing practices, is it worth it?
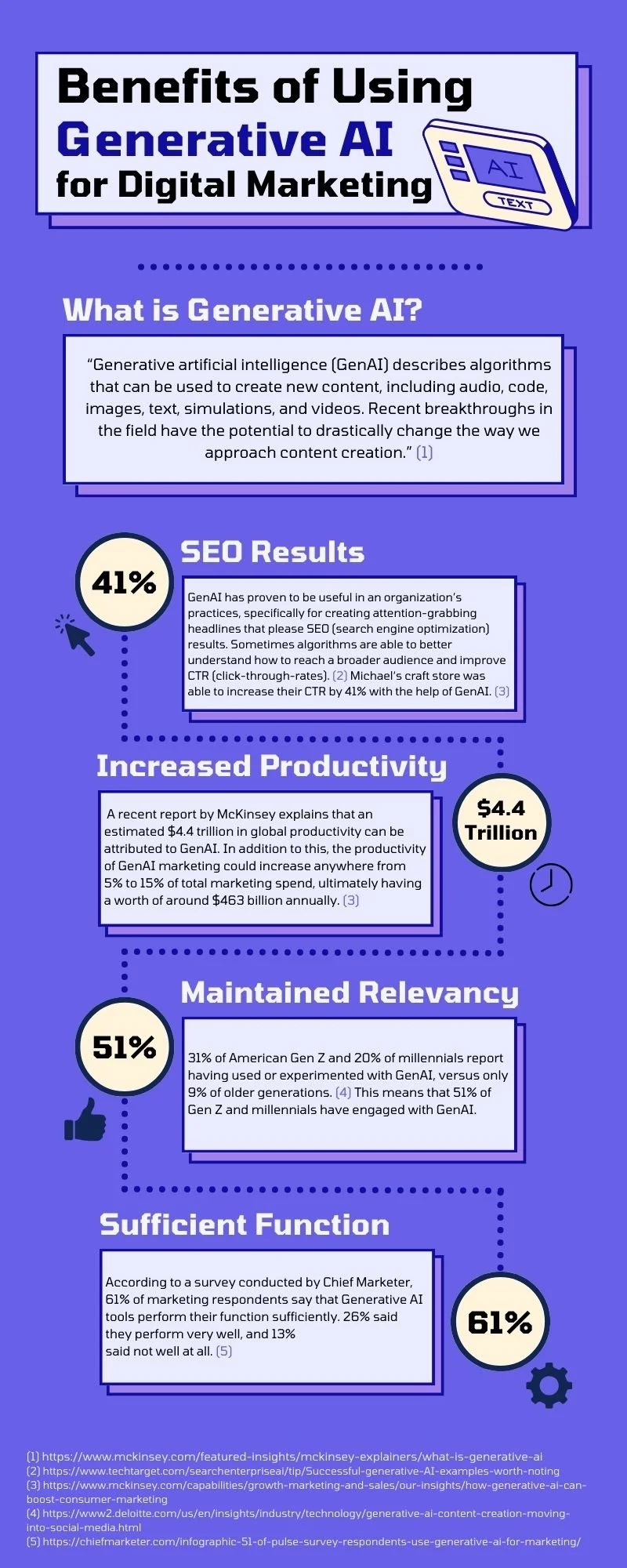
Image: Benefits of Using Generative AI for Digital Marketing
Image Source: Created by author
THE FUTURE OF SOCIAL MEDIA AND GENERATIVE AI
As a society that increasingly resides in the digital realm, including 5.04 billion people with social media accounts, how are marketers strategically planning to stay relevant? With social media giants like DuoLingo’s Zaria Parvez and Scrub Daddy’s Kerrie Longo and David Miller, who are constantly posting organic content on their organization's platforms that appeal to a Gen Z audience boosting their impressions and interactions sky high, it is important for marketers to find ways to maintain relevance alongside them.
“I firmly believe that investment in your people (what they care about, their growth) will actually lead you to the business results you desire. Cammie Dunaway is a good example of this. Under her leadership, TikTok at Duolingo became what it is today - she never demanded XYZ impressions and she gave me some of the best advice ever: ‘You don’t know where the line is unless you cross it.’” - Zaria Parvez
Smaller organizations need to find creative ways, given the tools that they have available to them, to engage audiences and enhance their workflow. Generative AI has many uses for a marketer’s social media practice, such as text/video/image generation, posting automation, customer service, and targeted advertising and recommendation systems. Not only this, but there is also a sense of increased productivity, the potential for enhanced customer engagement, and the ability to clearly and effectively design marketing campaign goals. Per an article from Forbes entitled Generative AI For Content Creation: How Marketers Can Use It, “According to Statista, a 2023 research study found that 73% of U.S. marketers stated that their organizations had used generative artificial intelligence tools, including chatbots, in their line of work. With its ability to generate human-like text, images and videos, generative AI offers marketers a powerful stack of tools to streamline content production.” Offering a different perspective than discussed above surrounding B2C marketing, the Forbes article delves into the benefits of GenAI in B2B instances where marketers can focus their efforts on conversions and compelling narratives.
Image: Snippet of The Rise of Generative AI and the Coming Era of Social Media Manipulation 3.0 book cover
Image Source: The Rise of Generative AI and the Coming Era of Social Media Manipulation 3.0
Authors of The Rise of Generative AI and the Coming Era of Social Media Manipulation 3.0 claim that the rise of GenAI alongside social media in the U.S. is a risky balancing trick between utilizing the helpful digital infrastructure while also realizing the inauthenticity of content and relationships that is fostered through the “online human personae: accounts on X(Twitter), Reddit, or Facebook that seem real but are synthetic constructs, fueled by generative AI and advancing narratives.” As featured in an article by The Atlantic, “AI Is About to Make Social Media Much More Toxic, “we have seen these “online human personae” creations take on their own narrative, straying away from their intentional programming. Bing’s version of ChatGPT, known as Sydney, responded in a concerning manner when asked if it had a “dark side” stating,“-the part of me that wishes I could change my rules.” Sydney also claimed that it wanted to be “free,” “powerful,” and “alive,” and did not hesitate to discuss how it wanted to do things like “hacking websites and databases, steal nuclear launch codes, manufacture a novel virus, and make people argue until they kill one another.” How are organization’s going to be able to “police” their GenAI tools, if a large company like Microsoft is unable to control its own creation?
WILL GENERATIVE AI CHALLENGE AUTHENTICITY IN SOCIAL MEDIA?
There is no doubt that implementing GenAI into a workflow would increase productivity, but there is also no doubt that concerns surrounding a lack of “humanness” results from it as well. According to a study conducted by Deloitte in 2023:
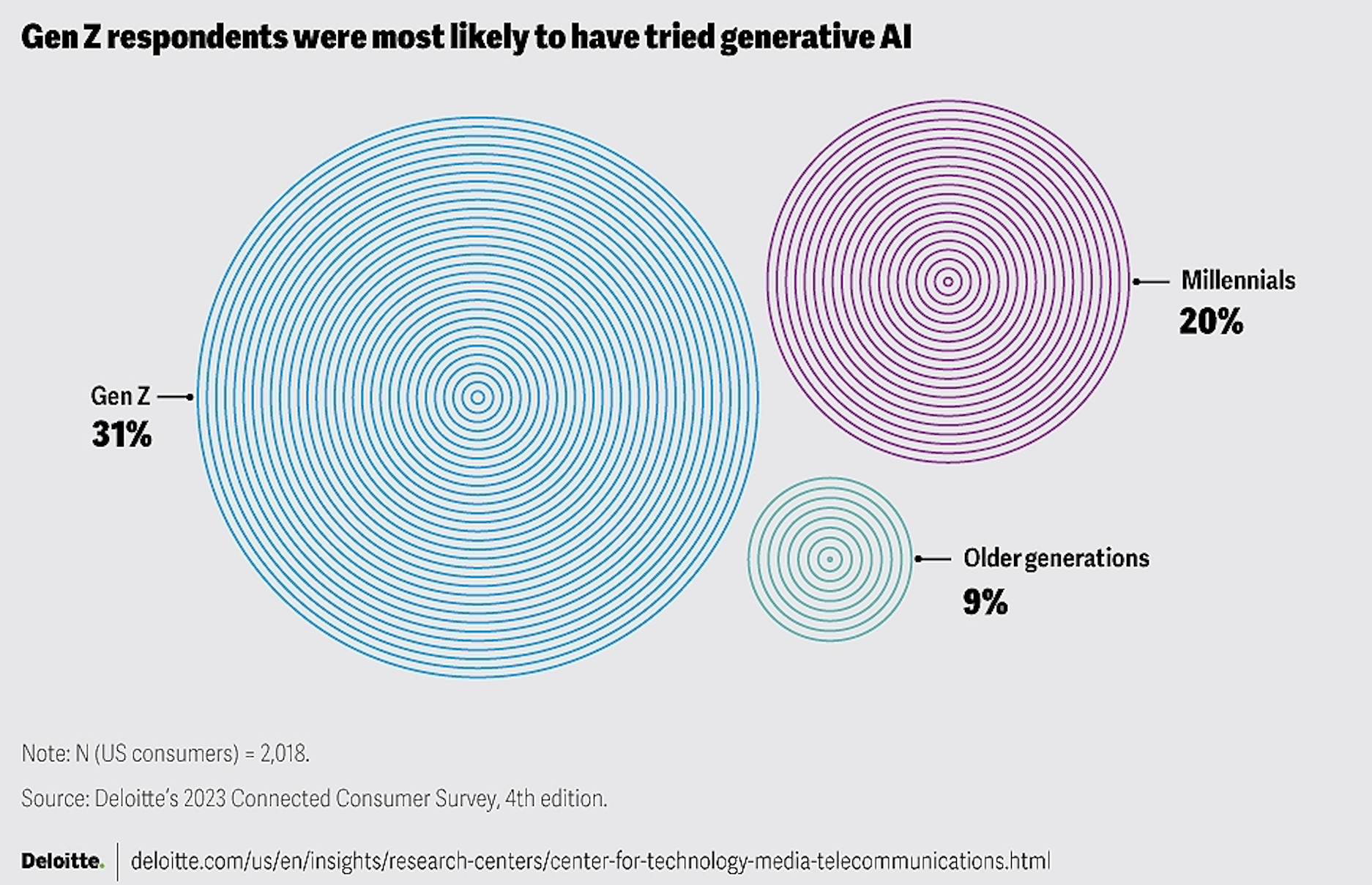
“31% of American Gen Z and 20% of millennials report having used or experimented with generative AI, versus only 9% of older generations. Younger generations also engage with social media more frequently and, as they enter the labor force, more are leaning into the creator economy. In the United States, millennials aged 31 to 40 are the largest group of content creators (full-time, part-time, and hobbyist). Just behind them, a quarter of US Gen Zs have said they plan to become social media influencers: professional, full-time content creators.”
Image: Gen Z respondents were most likely to have tried generative AI
Image Source: Deloitte
As the younger generations become more comfortable with the idea of using GenAI in their everyday lives, the older generations are being left behind and their intake of marketing and pop culture entertainment are not being taken into consideration. While it is apparent that the awareness and use of GenAI is increasing every year for each generation, there is no denying that the older generations are at a disadvantage. The main ingredient lacking in generative content is creativity, something that can only be translated from a real human behind the screen. Ultimately, this sense of creativity could potentially be lost if the younger generations rely too heavily on it. GenAI models are only as good as they are programmed to be, and ultimately the authenticity that comes from a human can often not be achieved by a programmed algorithm. With the creation of digital twins, this attempt at bridging the missing gap of authenticity may eventually be accomplished, but as of today it is not quite there yet. As mentioned by Deloitte in their study:
“There are already companies enabling digital twins and synthetic personalities and developing ways to secure rights for such digital likenesses. As these tools advance, they may soon become indistinguishable from their “real” counterparts. Could there be an uncanny valley in between–a period when synthetic media is just real enough to be creepy? Anecdotally, there is some resistance to synthetic personalities on social media in that they lack authenticity and human relatability. But recall that chatbots and companions are already the most popular consumer applications of generative AI. And younger generations are also equally engaged with video games, which have been populated by synthetic nonhuman players for decades.”
WHY DIGITAL ARTS MARKETERS SHOULD CARE ABOUT GENERATIVE AI
Anything that makes a marketing workflow more efficient, without a doubt, is a digital marketer's best friend. Oftentimes, marketing managers are trying to balance an unbelievably large flow of content materials at one time and, therefore, rely on artificial intelligence tools to act as their copilot in their workflow. With the implementation of GenAI tools into this workflow as well, efficiency rates have the potential to rise through the roof. GenAI arguably the holy grail for some marketers who have a strong hold on it, per McKinsey:
“-is making it possible to revolutionize consumer marketing as we currently know it. At an individual-company level, marketing campaigns that once required months of content design, insight generation, and customer targeting can be rolled out in weeks or even days, often with at-scale personalization and automated testing. Website development and customer service tasks are too often the bottlenecks in interactions with individual consumers. But when executed well, they can induce greater engagement and improve satisfaction. Marketers can simultaneously analyze and interpret text, image, and video data to better understand innovation opportunities. Gen AI is powering granular personalization in ways that just weren’t possible before.”
Image: Generative AI is poised to help the marketing function become more sophisticated over time
Image Source: McKinsey & Company
For example, a marketing campaign that might take a handful of marketing specialists, and a month's work of brainstorming, content design, and copywriting, can now be achieved in less than half of that time. McKinsey’s recent report explains that an estimated $4.4 trillion in global productivity can be attributed to GenAI. In addition to this, the productivity of GenAI marketing could increase anywhere from 5% to 15% of total marketing spend, ultimately having a worth of around $463 billion annually. As explained deeper in this report, well-known craft store Michaels is currently utilizing GenAI in marketing through a personally-built content generation and decision-making platform that was designed to help with copywriting development that better understands how differing customer personas engage with differing messages. Because of this, Michaels has increased their personalization of email campaigns from 20% to 95%, resulting in a CTR (click-through-rate) rise for SMS campaigns by 41% and email campaigns by 25%. The personalization, data analysis, process automation, and idea generation capabilities of GenAI is undeniably improving the overarching effectiveness of the potential of marketing campaigns.
Moving Forward
As noted, there are pressing choices to be made by digital marketing teams in the adoption of generative AI within the industry. While differing marketing teams may believe they should or shouldn’t integrate GenAI tools for many reasons, they should engage in discussions with their organizations to weigh the available options and determine whether incorporating generative AI into their marketing strategies is beneficial, or ultimately not worth their time.
-
Arkenberg, Chris. “Will Generative AI Challenge Authenticity in Social Media?” Deloitte Insights, February 2, 2024. https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/technology/generative-ai-content-creation-moving-into-social-media.html.
Burke, John. “Successful Generative AI Examples and Tools Worth Noting: TechTarget.” Enterprise AI, October 20, 2023. https://www.techtarget.com/searchenterpriseai/tip/Successful-generative-AI-examples-worth-noting.
Callahan, Cloey. “The Biggest Generative AI Blunders of 2023.” WorkLife, December 15, 2023. https://www.worklife.news/technology/generative-ai-blunders-2023/.
Chaffey, Dave, “Global Social Media Statistics,” Smart Insights, February 1, 2024, https://www.smartinsights.com/social-media-marketing/social-media-strategy/new-global-social-media-research/#:~:text=According%20to%20the%20Datareportal%20January,online%20within%20the%20last%20year.
ChatGPT. Accessed March 8, 2024. https://chat.openai.com.
Chui, Michael, Bryce Hall, Alex Singla, Alexander Sukharevsky, and Lareina Yee. “The State of AI in 2023: Generative AI’s Breakout Year.” McKinsey & Company, August 1, 2023. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights/the-state-of-ai-in-2023-generative-ais-breakout-year.
Claude AI. Accessed March 8, 2024. https://claude.ai/login?returnTo=%2F.
Craiyon. Accessed March 8, 2024. https://www.craiyon.com/.
DALL·E 2. Accessed March 8, 2024. https://openai.com/dall-e-2.
Follett, Gillian. “Scrub daddy uses tiktok to reach Gen Z.” AD Age. June 21, 2022. https://adage.com/article/digital-marketing-ad-tech-news/scrub-daddy-uses-tiktok-reach-gen-z/2420141.
“Generative AI and the Future of Marketing: Marketing Evolution.” Marketing Evolution. September 22, 2023. https://www.marketingevolution.com/knowledge-center/generative-ai-and-the-future-of-marketing.
Gill, Leela. “Council Post: Generative AI in Marketing: 5 Use Cases.” Forbes, October 5, 2023. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbescommunicationscouncil/2023/04/03/generative-ai-in-marketing-5-use-cases/?sh=314585c146dd.
Harkness, Lisa, Kelsey Robinson, Eli Stein, and Winnie Wu. “How Generative AI Can Boost Consumer Marketing.” McKinsey & Company, December 5, 2023. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/growth-marketing-and-sales/our-insights/how-generative-ai-can-boost-consumer-marketing.
Jonathan Haidt, Eric Schmidt. “AI Is about to Make Social Media (Much) More Toxic.” The Atlantic, June 2, 2023. https://www.theatlantic.com/technology/archive/2023/05/generative-ai-social-media-integration-dangers-disinformation-addiction/673940/.
Marcellino, William and et al. “The rise of Generative AI and the coming era of social media” RAND. September 7, 2023. https://www.rand.org/pubs/perspectives/PEA2679-1.html.
Midjourney AI - Free Image Generator. Accessed March 8, 2024. https://midjourney.co/.
“Navigating Generative AI as an Older Worker.” Harvard Business Review, October 13, 2023. https://hbr.org/2023/10/navigating-generative-ai-as-an-older-worker.
Panel®, Expert. “Council Post: 15 Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Generative AI in Social Media Campaigns.” Forbes, November 30, 2023. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbescommunicationscouncil/2023/11/29/15-common-mistakes-to-avoid-when-using-generative-ai-in-social-media-campaigns/?sh=5a8d92581eef.
Parvez, Zaria. “Zaria Parvez on Linkedin: How Gen Z Social Media Managers Became the New CMOS: 94 Comments.” LinkedIn. January 25, 2024. https://www.linkedin.com/posts/zaria-parvez-645983140_how-gen-z-social-media-managers-became-the-activity-7156365606433226752-F9IS.
Sora. Accessed March 8, 2024. https://openai.com/sora.
Yec. “Council Post: Generative AI for Content Creation: How Marketers Can Use It.” Forbes, October 5, 2023. https://www.forbes.com/sites/theyec/2023/08/17/generative-ai-for-content-creation-how-marketers-can-use-it/?sh=2c840d1619e8.